Vegetables


Vegetables
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just beginning, explore our guides and publications on techniques to cultivate a thriving vegetable garden in Wisconsin.
Vegetable Videos

Find recorded Extension video programs ranging on topics from fundamentals of shrub pruning to proper tree planting by clicking the button below.
General Vegetable Resources
Discover a variety of resources on growing vegetables. Dive into guides, articles, and websites below!

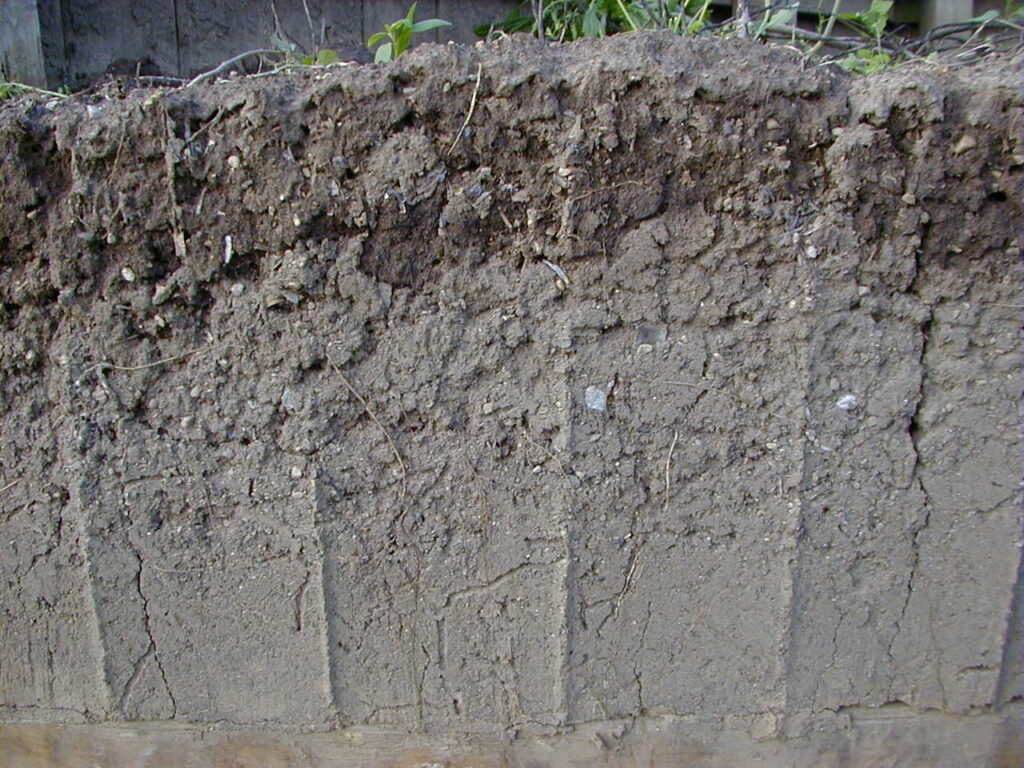
Soil Testing
Find links to the UW Soil and Forage Lab for the submission form and instructions to test your soil!
Hardiness Maps
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is the standard by which gardeners and growers can determine which perennial plants are most likely to thrive at a location.
The Vegetable Garden
This mini-book covers all you need to know from planning to planting!
Seed Starting
Whether flowers, vegetables, or herbs, consider the factors in this publication before starting!
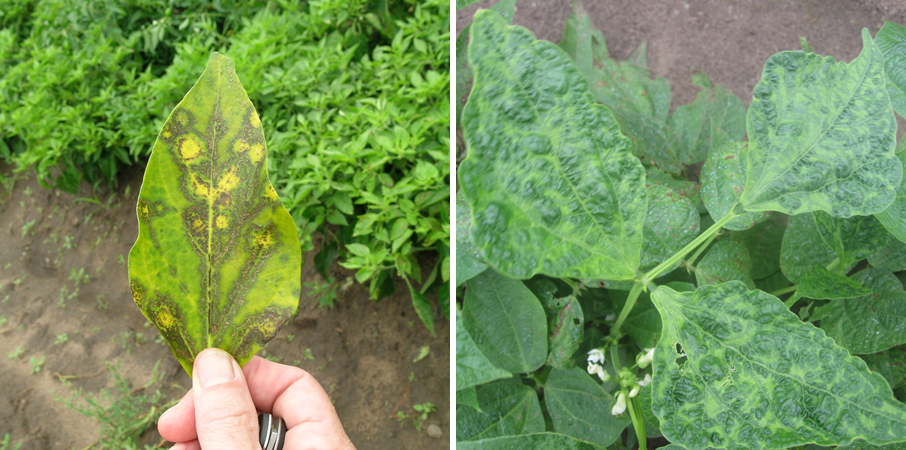
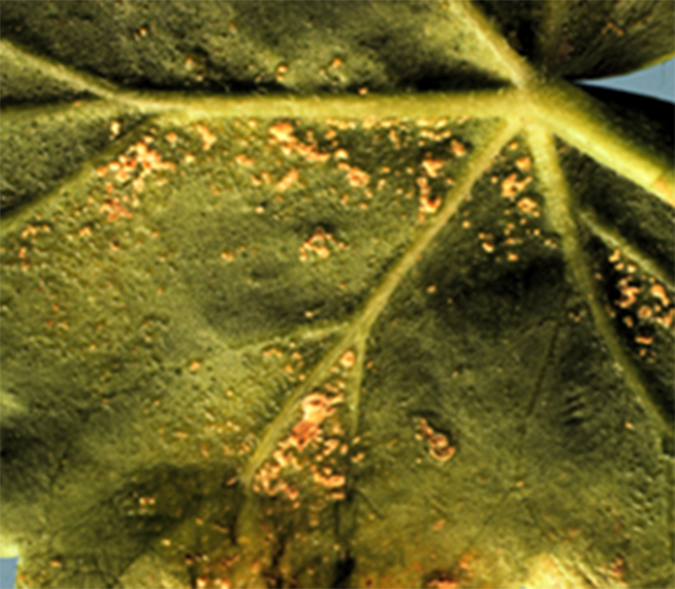
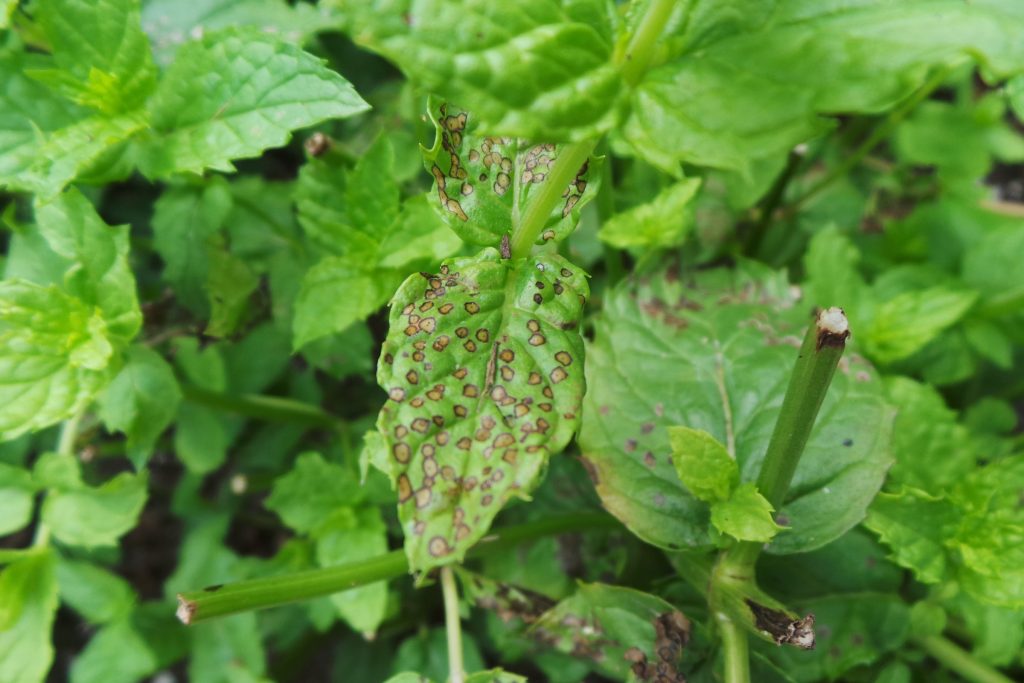
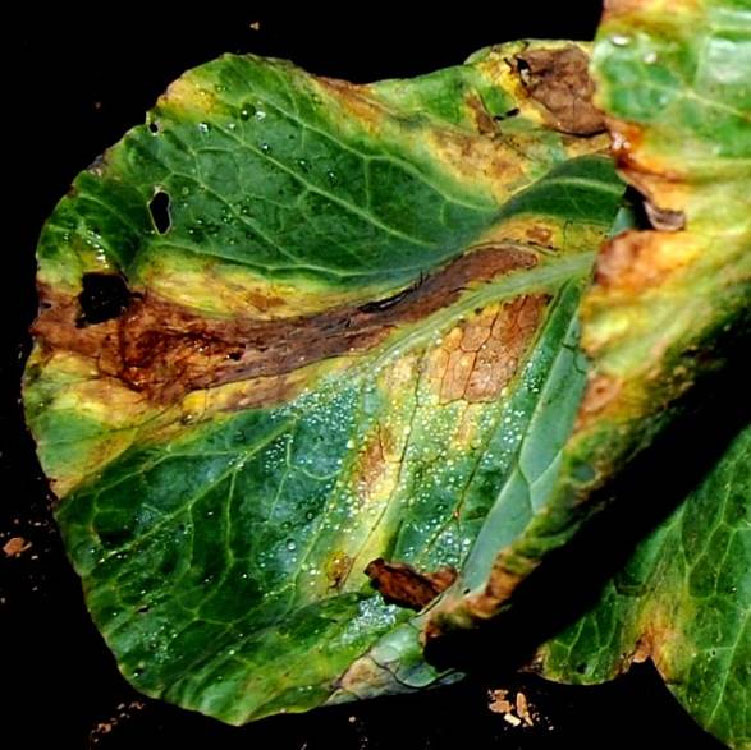
Vegetable Crop Pathology
UW Madison has an ongoing research program on vegetable crop pathology. Find resources ranging from weather and disease risk models to a weekly vegetable crop newsletter during the growing season.
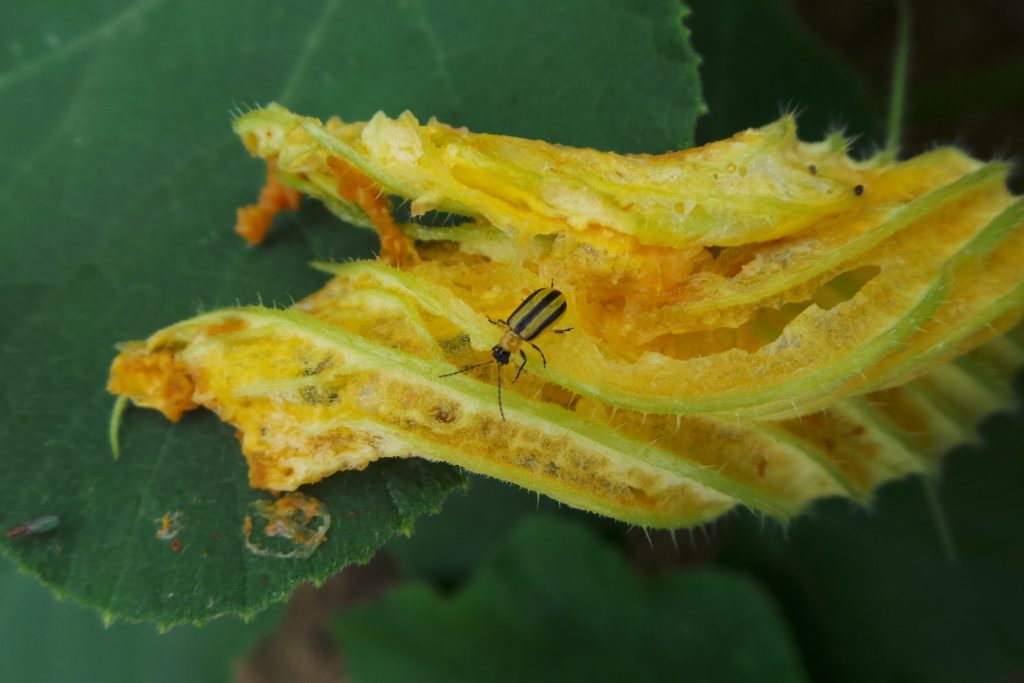
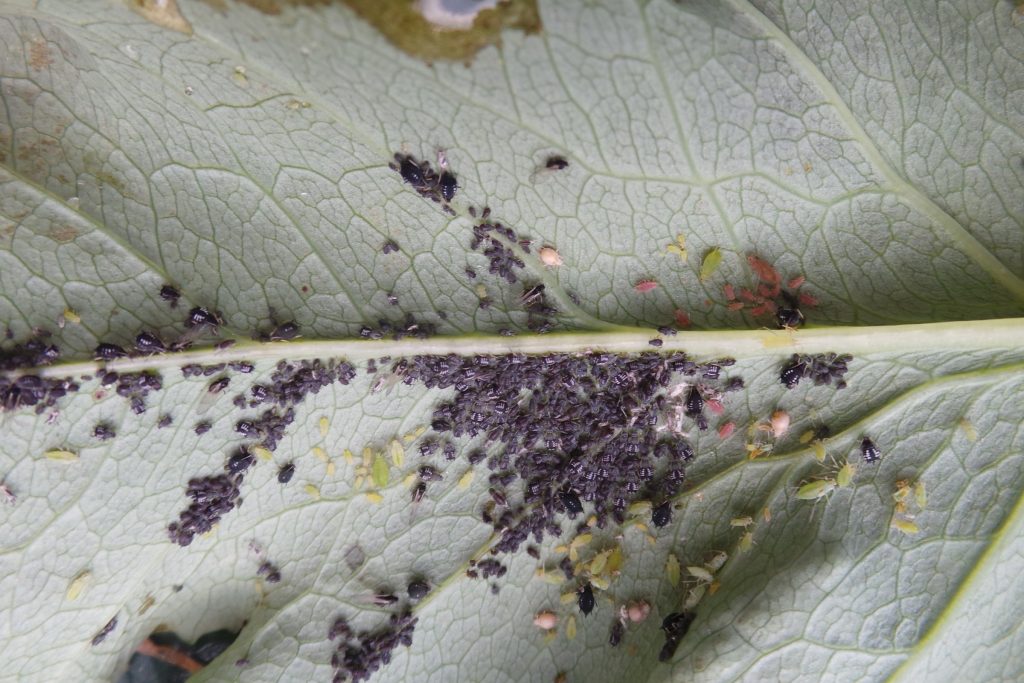
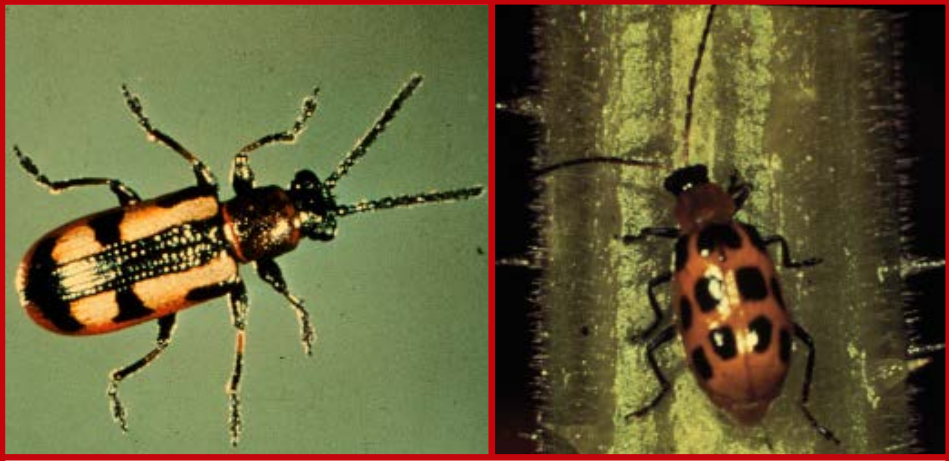
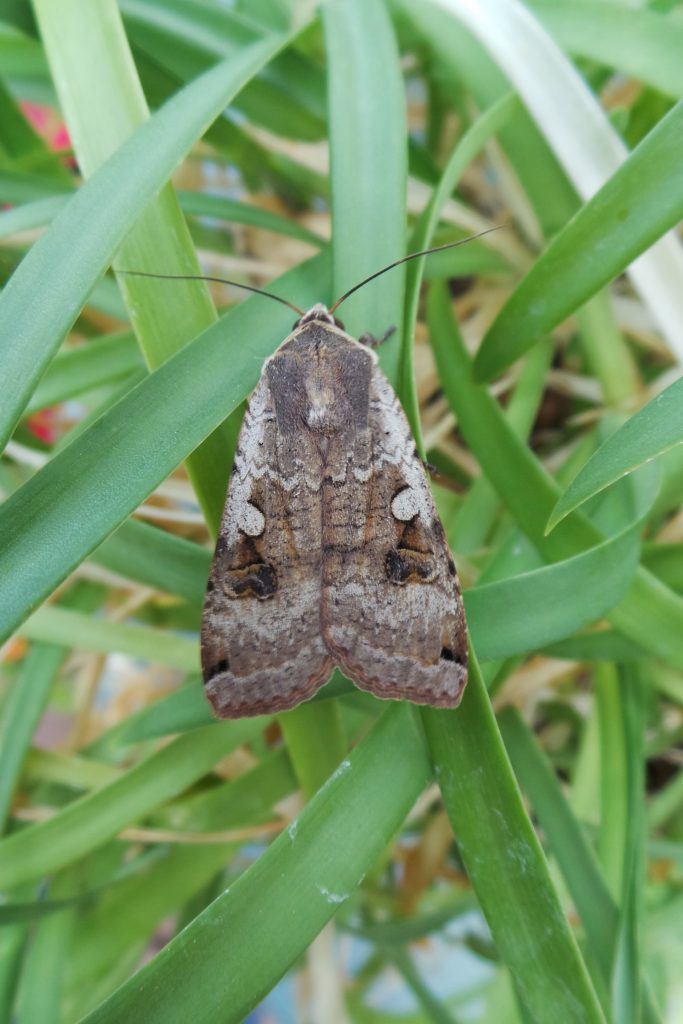
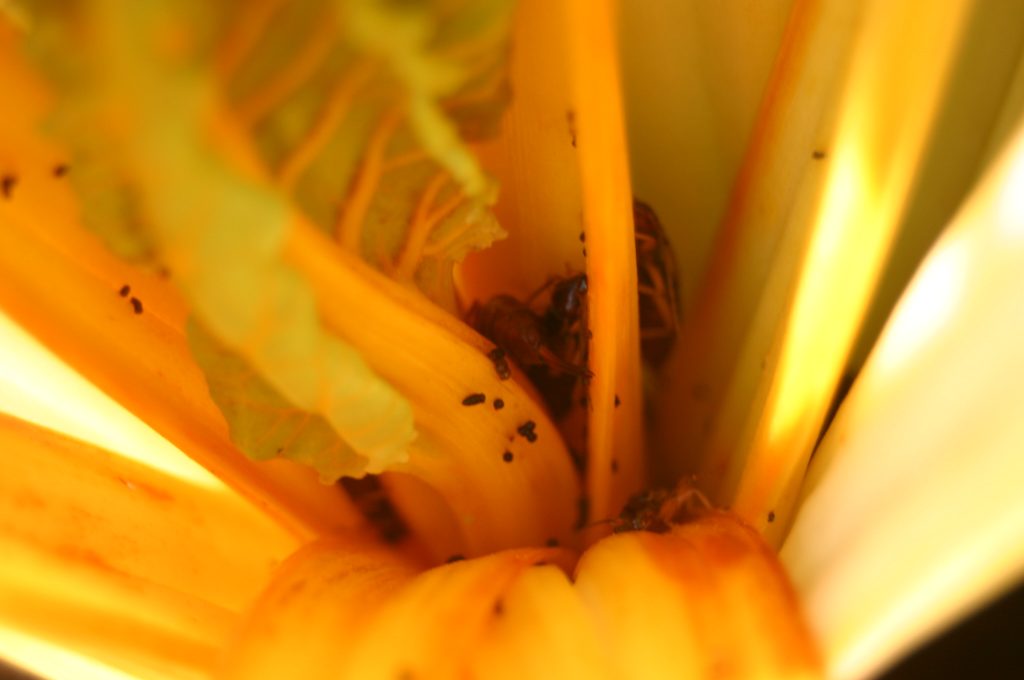
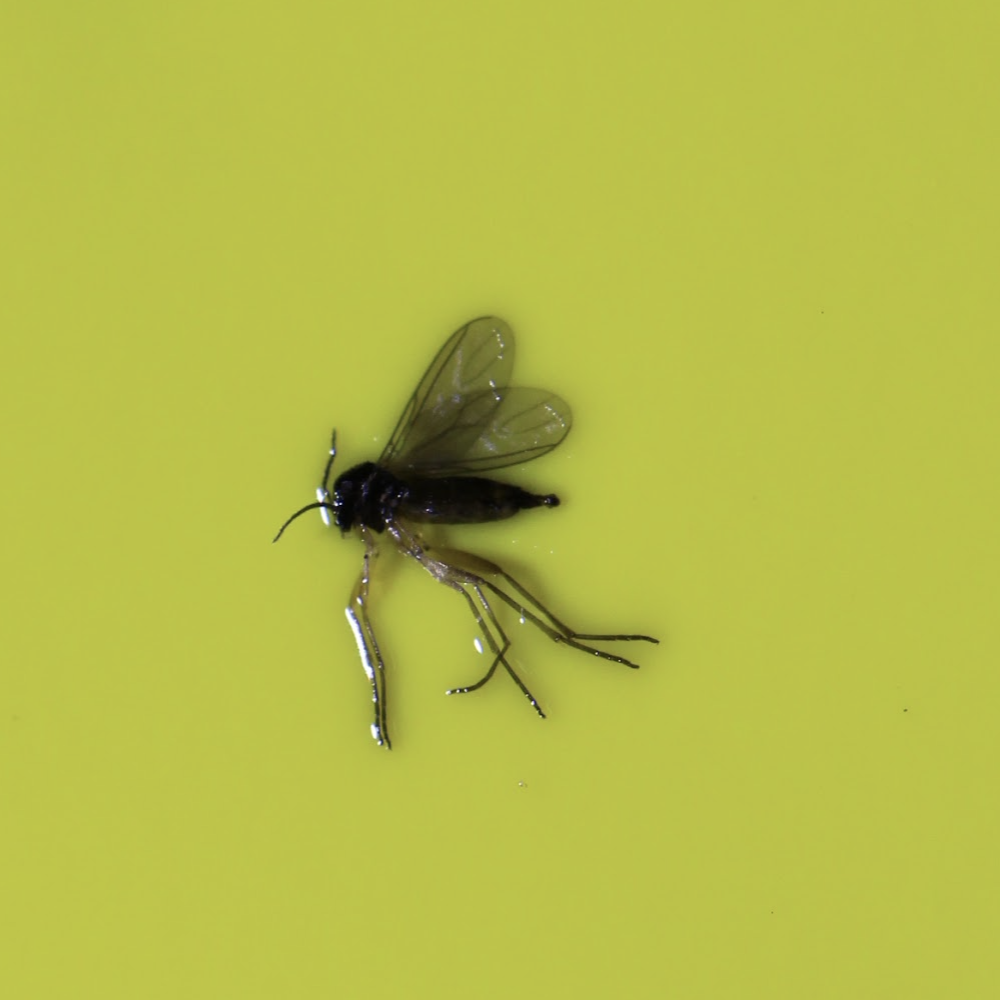
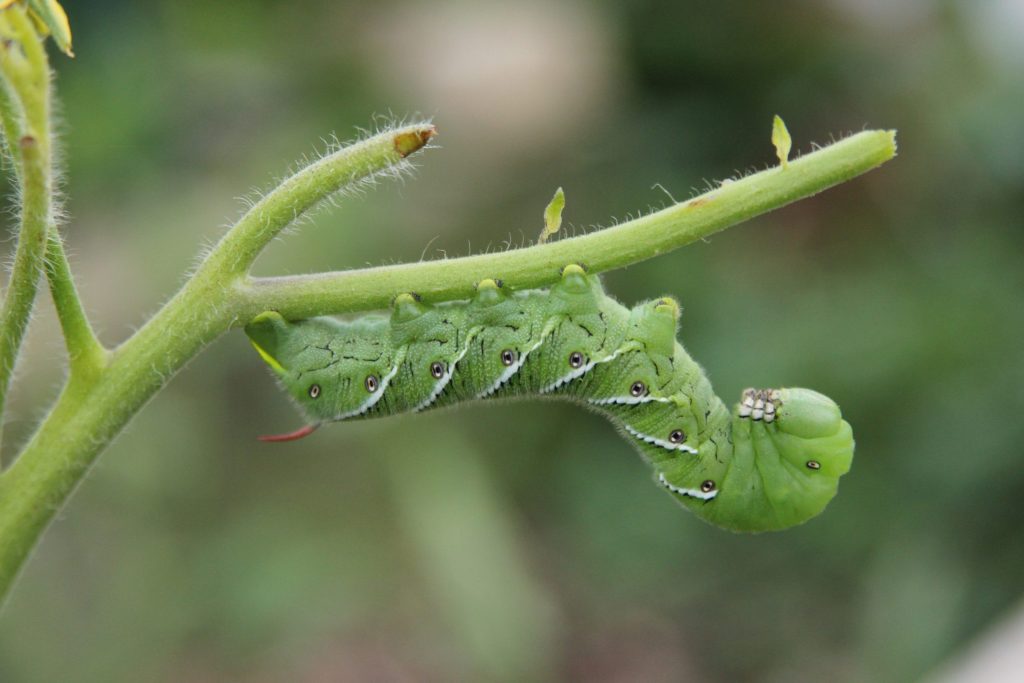
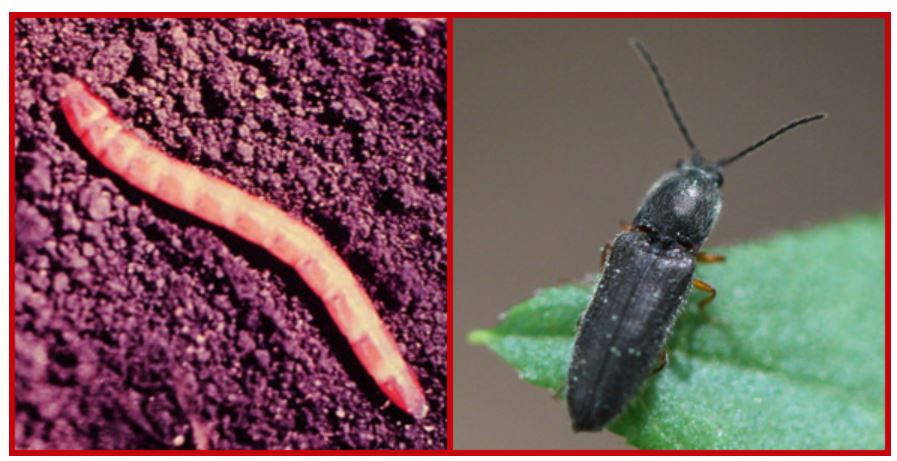
Vegetable Crop Entomology
This UW Madison research program centers around the ecology and management of insects of commercial and fresh market vegetable crops.
Photo left: Radishes and beets
Popular Vegetable Articles
Discover our most popular vegetable articles below!

Beginning Vegetable Garden Basics: Site Selection & Soil Preparation
This fact sheet focuses on how novice gardeners can select and prepare their garden site to ensure maximum success.
Container Gardening
Live in an apartment or condo? You can still raise a garden’s worth of flowers or vegetables in pots and other containers by mastering these methods.
Raised Beds and Containers for Community Gardens
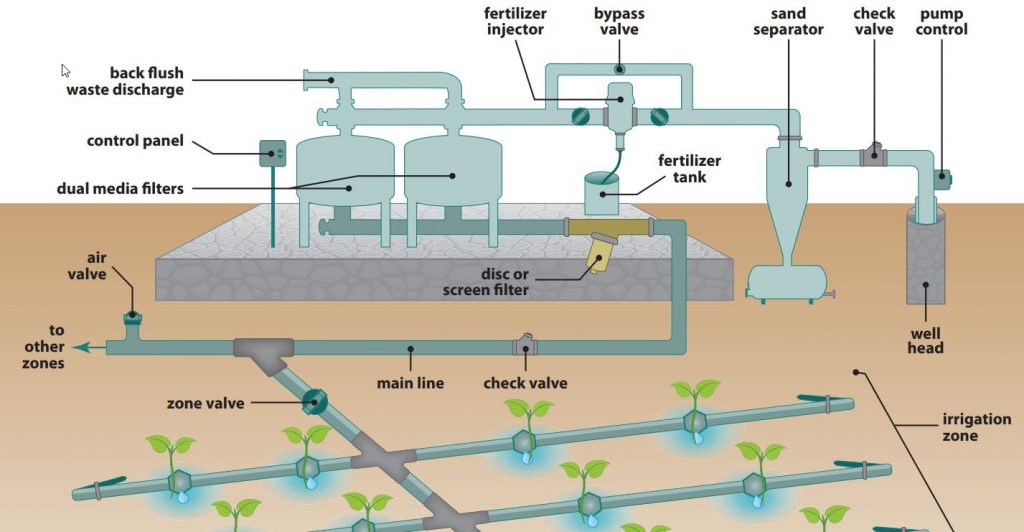
Above-ground gardening offers access and ease for community gardeners of all ages and abilities. Topics covered include raised bed construction, container selection, donated materials, soil, planting, and irrigation.
Tomato Pruning
Are you growing indeterminant tomatoes? Learn this pruning technique to improve fruit production.
Using Manure in the Home Garden
Thinking about using animal manure in your home garden this season? It can be a valuable soil amendment, but there are important things to know about keeping yourself and your plants healthy.
Using Wood Ash in the Home Garden
Wood ash can be a valuable source of certain nutrients and can also be used to modify soil pH. However, it needs to come from an appropriate source and its use should be based on recommendations from soil testing.
Photo left: Swiss Chard
Articles
Click on each section below to browse a list of categorized articles.
Site Selection & Preparation
Selecting & Planting
Care & Maintenance
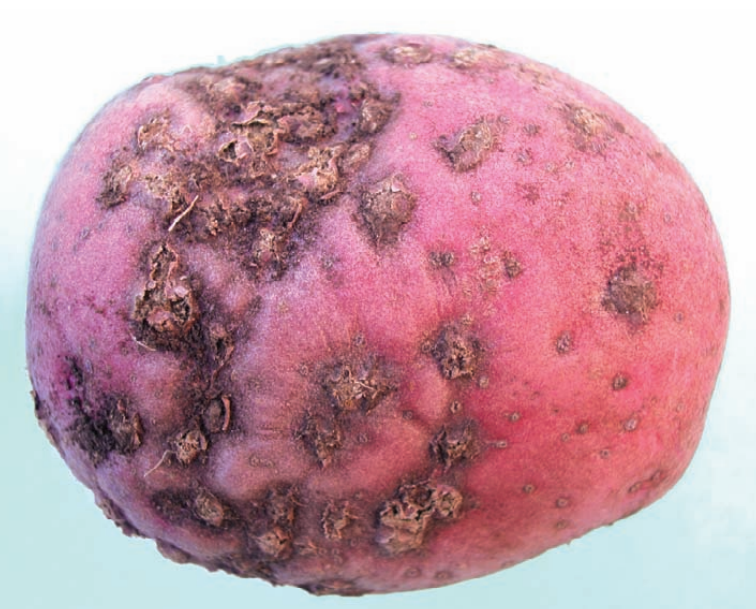
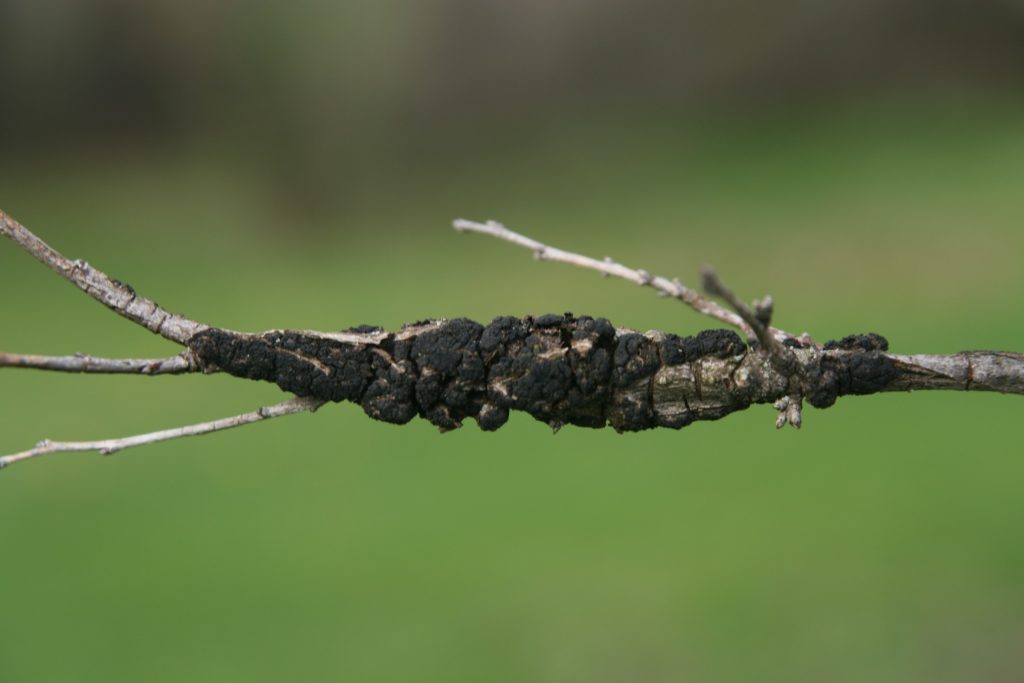
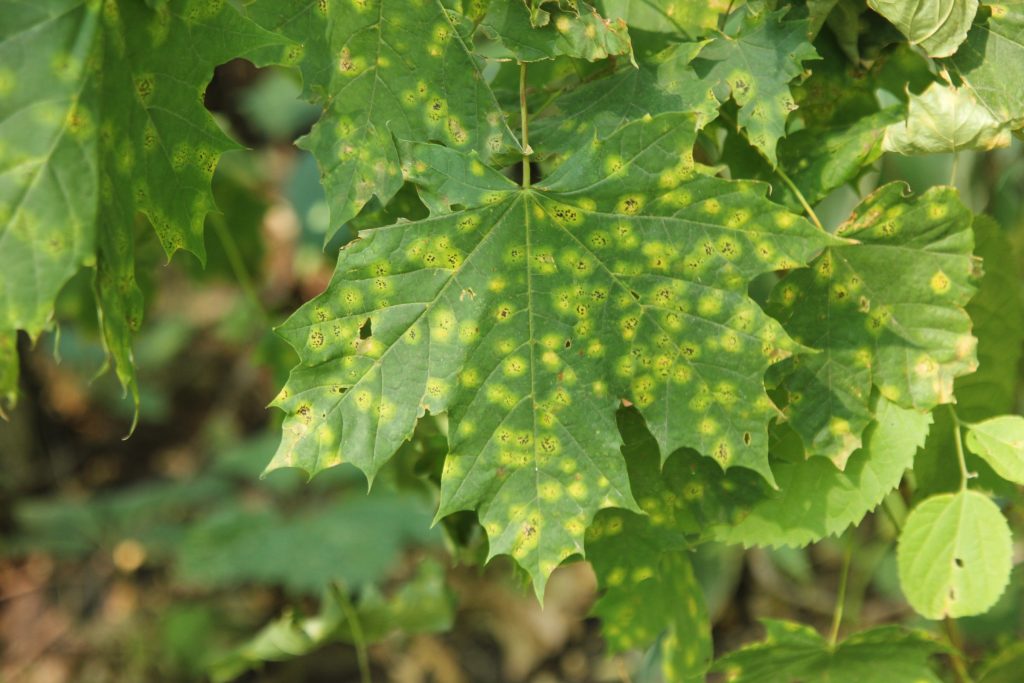
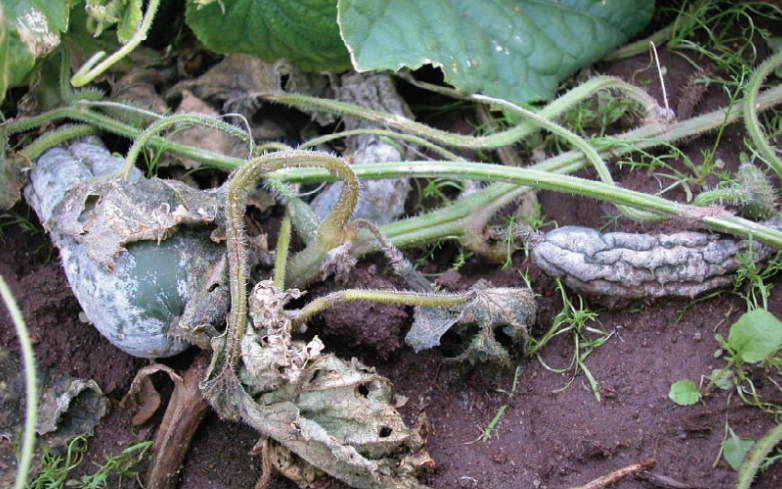
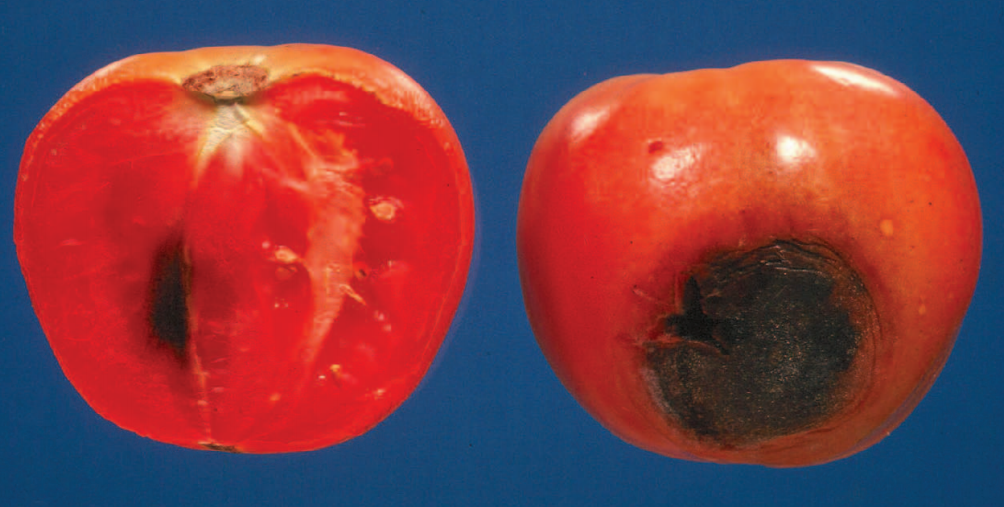
Diseases & Disorders
Insects
Harvest
Other
Submit additional lawn, landscape and gardening questions using our Ask Your Gardening Question form.