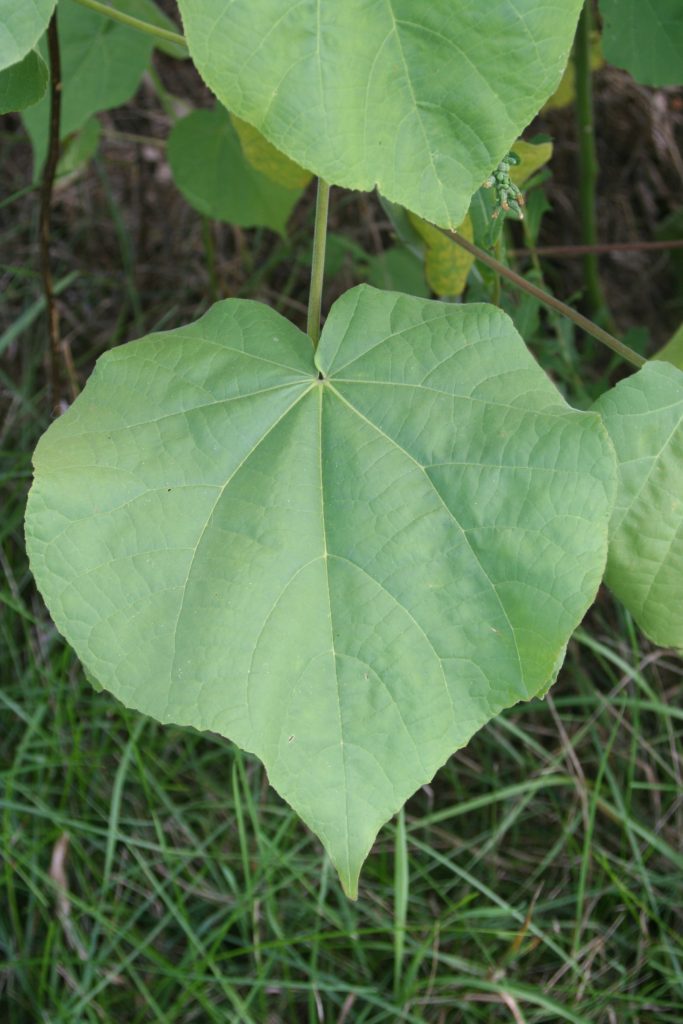
Weeds & Invasive Plants
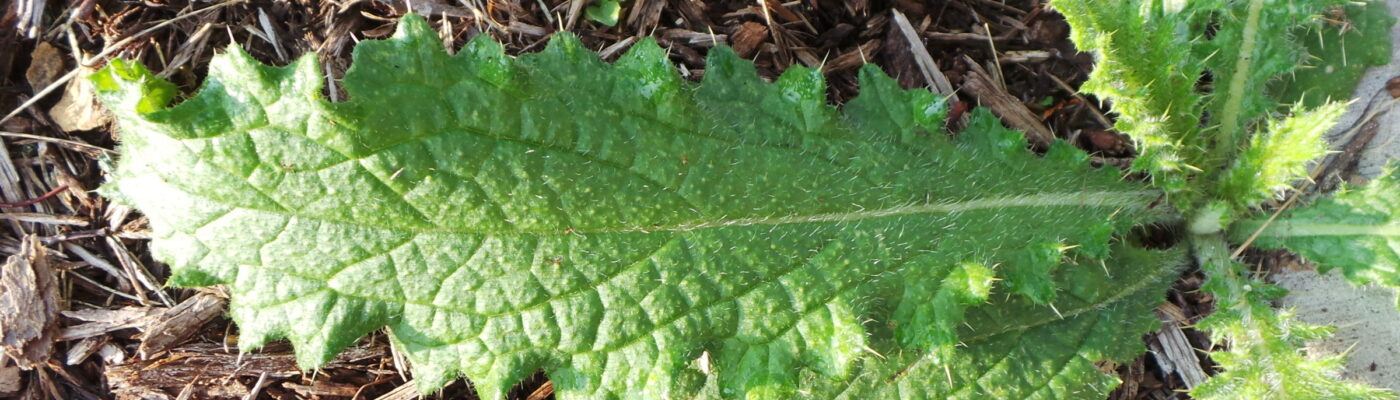
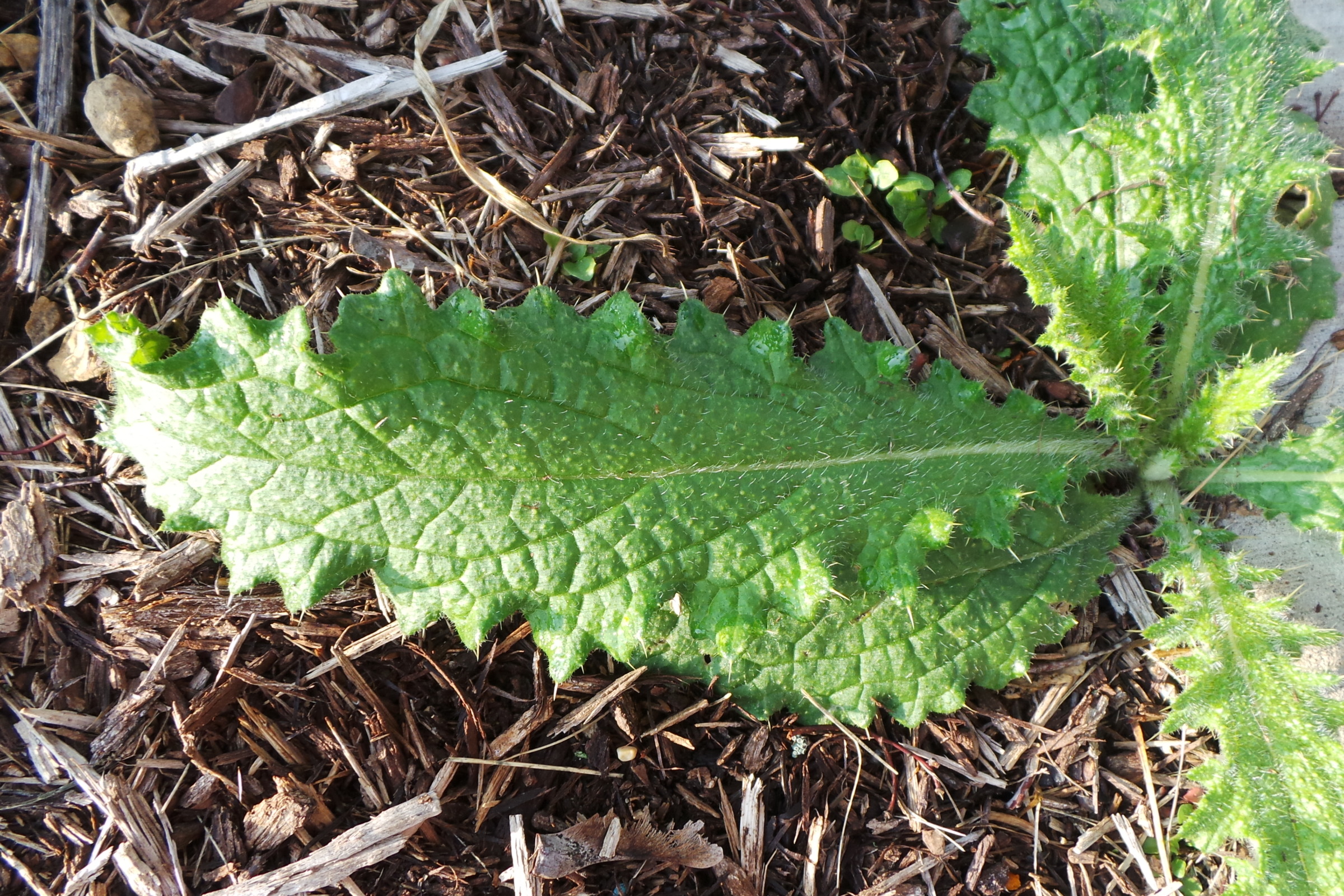


Weeds & Invasive Plants
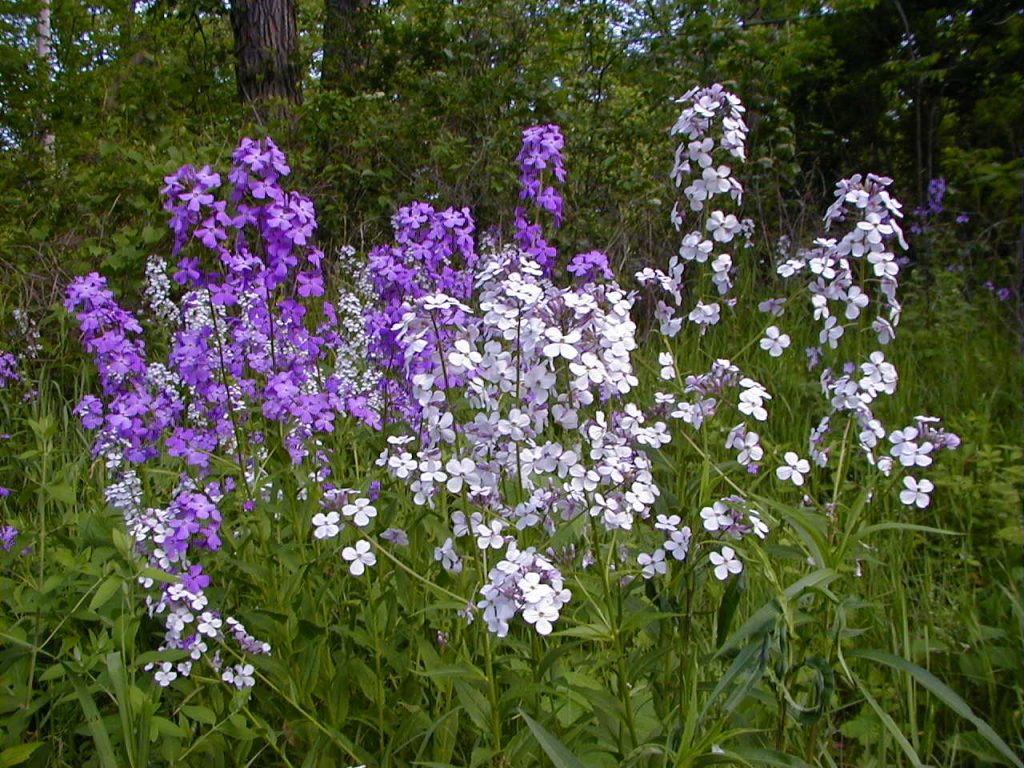
A weed is any plant growing in a location where it is not wanted and is often in competition with desirable cultivated plants. Use the guide below to learn more about common weeds of Wisconsin.
Invasive Weed Identification Videos

The Renz Lab has produced a series of short videos instructing viewers how to correctly identify a variety of terrestrial invasive plant species found in Wisconsin.
General Weeds Resources
Discover a variety of resources on weeds. Dive into guides, articles, and websites below!

DNR Invasive and Regulated Plants List
Code NR 40 makes it illegal to possess, transport, transfer or introduce certain invasive species in Wisconsin without a permit.
Invasive Plant Management
A series of factsheets discussing the identification and control of common invasive plant species. Mechanical, cultural, and chemical control methods are discussed in detail.
Wisconsin Terrestrial Invasive Plant Presence (WISTIPP) Viewer
An online interactive map that makes it easy to view and download terrestrial invasive plant reports in Wisconsin.
Weed Management Herbicide Trials
Weed management reports intended to help farmers, restoration ecologists, landowners, and researchers stay up to date on the latest and most effective herbicides for their land management goals.
10 Things to Consider for Weed Management When Establishing Pollinator Plantings
In this video, you will learn about Mark Renz’s research on weed management options and what factors you should consider when planning and establishing pollinator plantings.
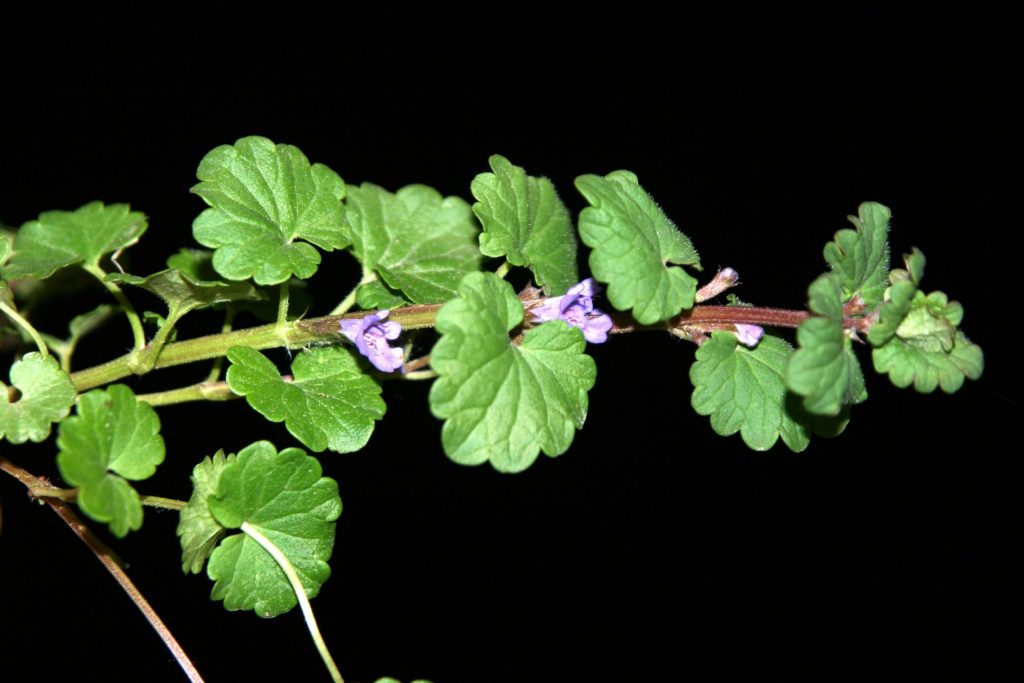
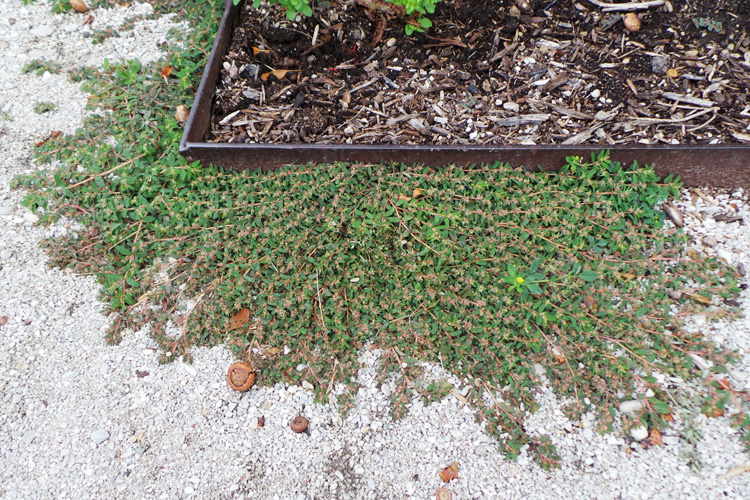
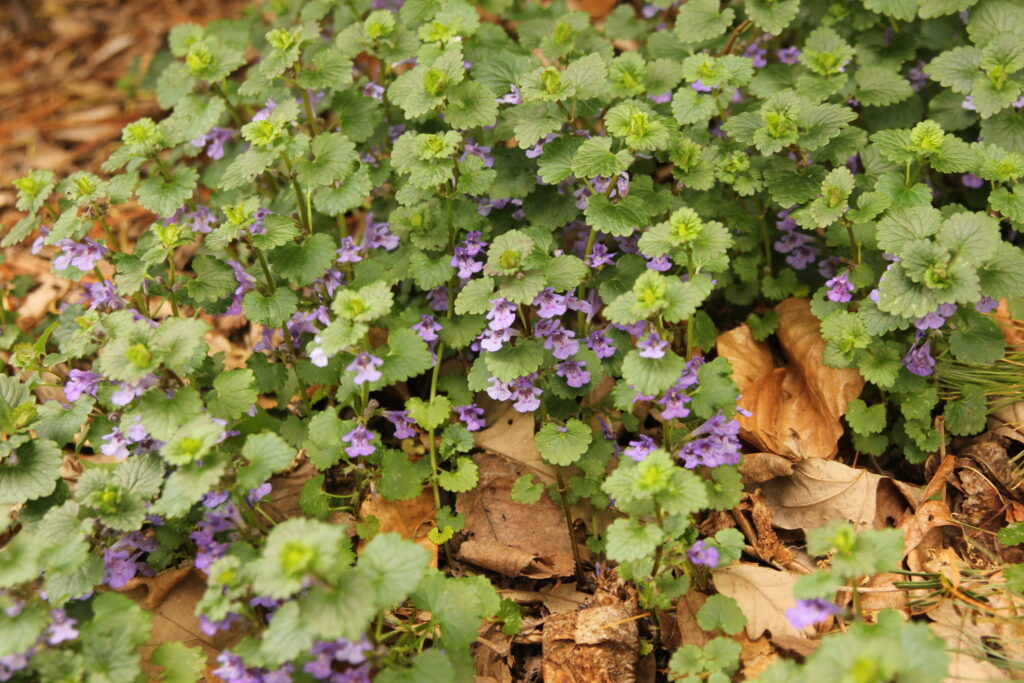
Photo left: Creeping Charlie
Popular Weed Articles
Discover our most popular weed articles below!

Controlling Creeping Charlie
A difficult to control perennial weed in the mint family that spreads by seeds, rhizomes and creeping stems that root at the nodes.
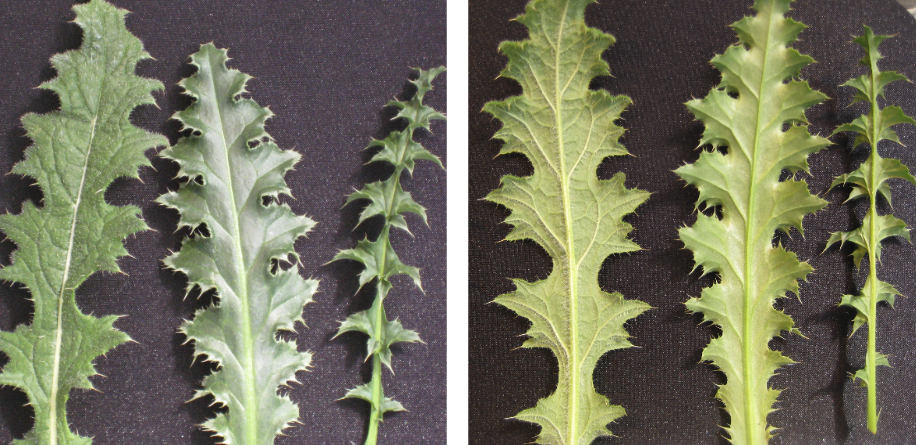
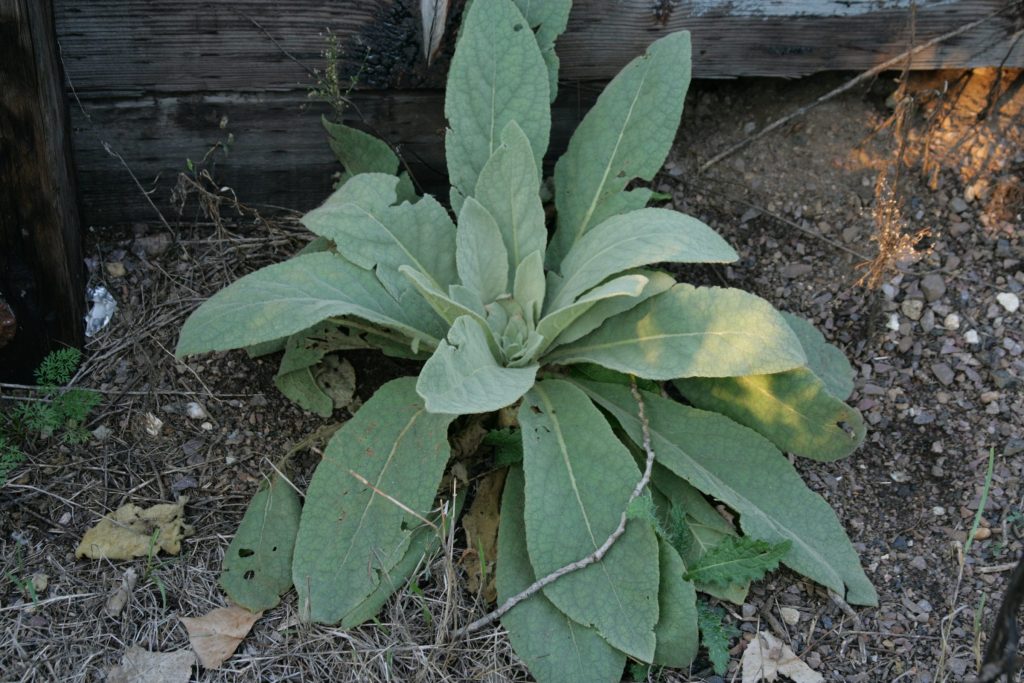
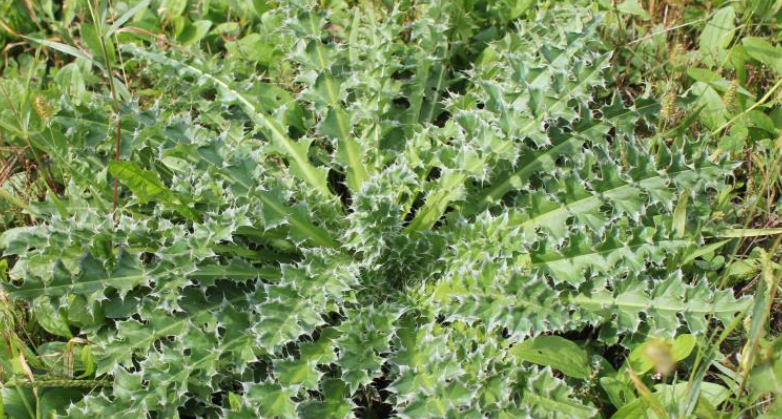
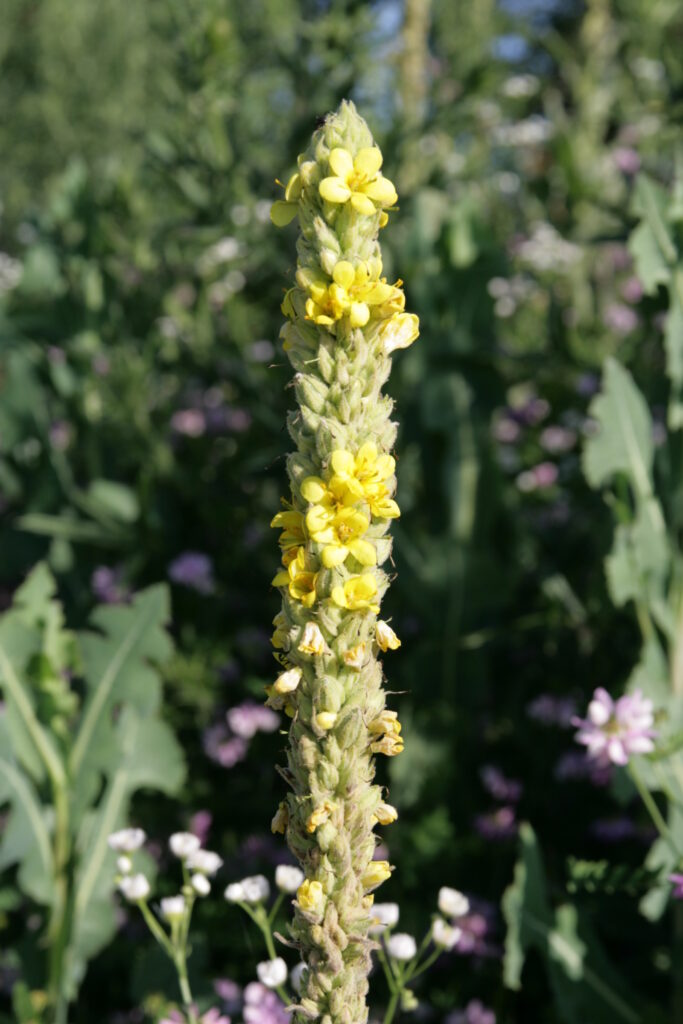
Common Mullein
An herbaceous biennial or short-lived perennial with a deep tap root.
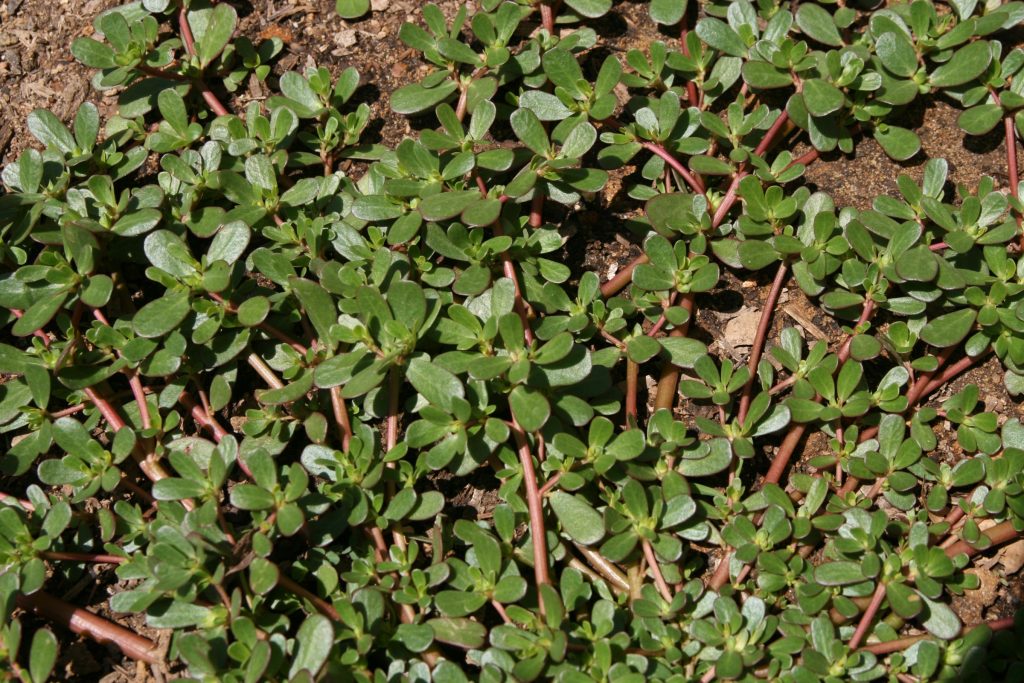
Common Purslane
A highly variable, weedy plant in the purslane family (Portulacaceae) with a wide distribution.
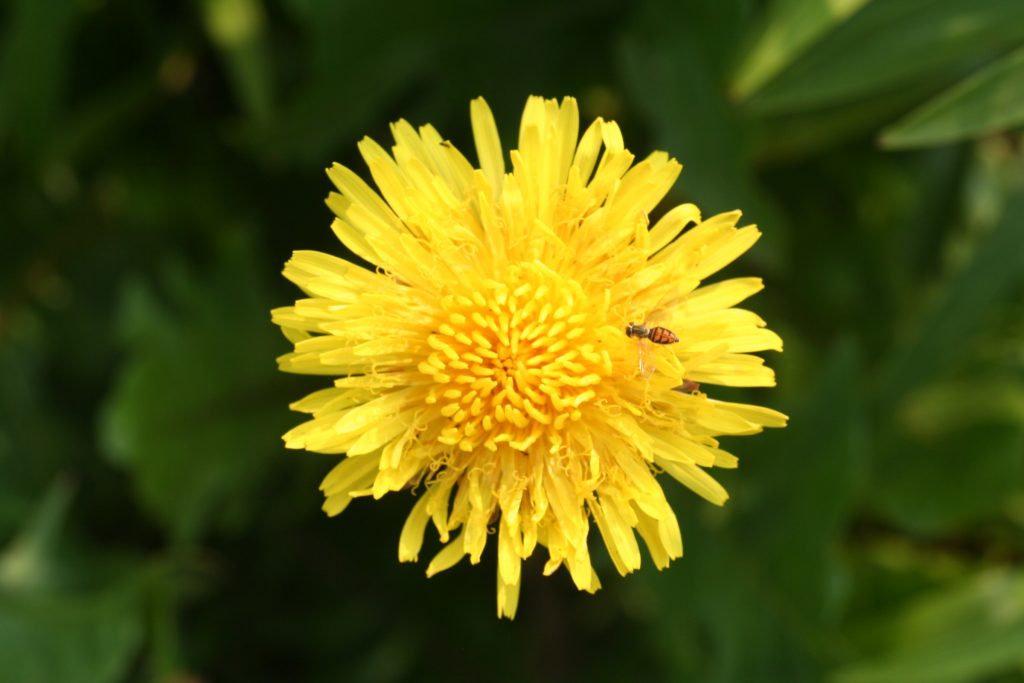
Dandelion
A common plant native to Eurasia but has naturalized in all parts of the Northern Hemisphere.
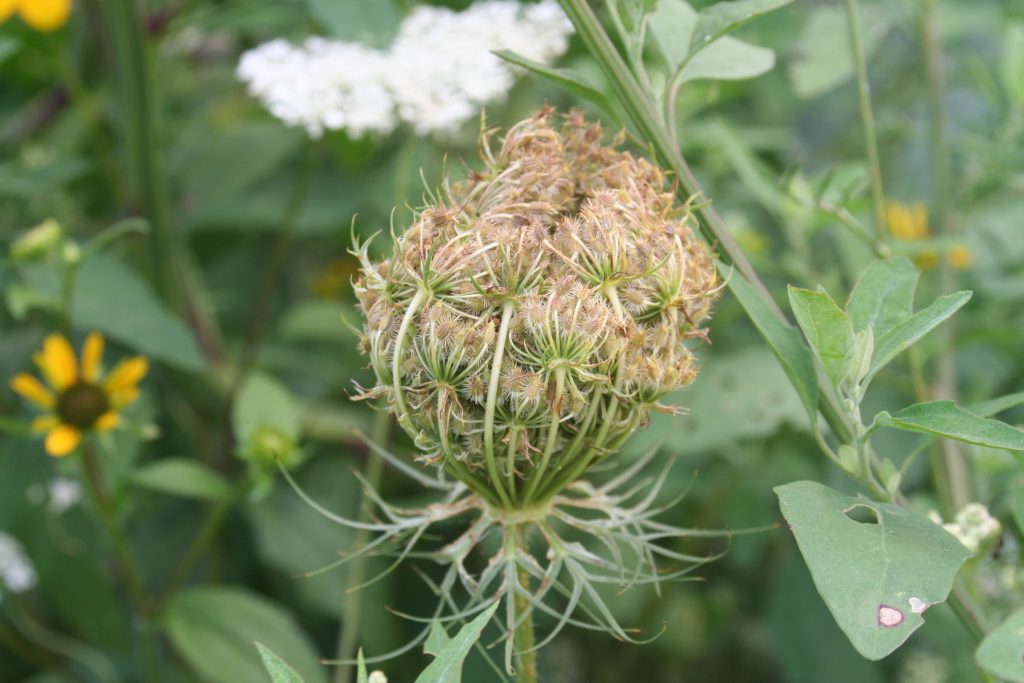
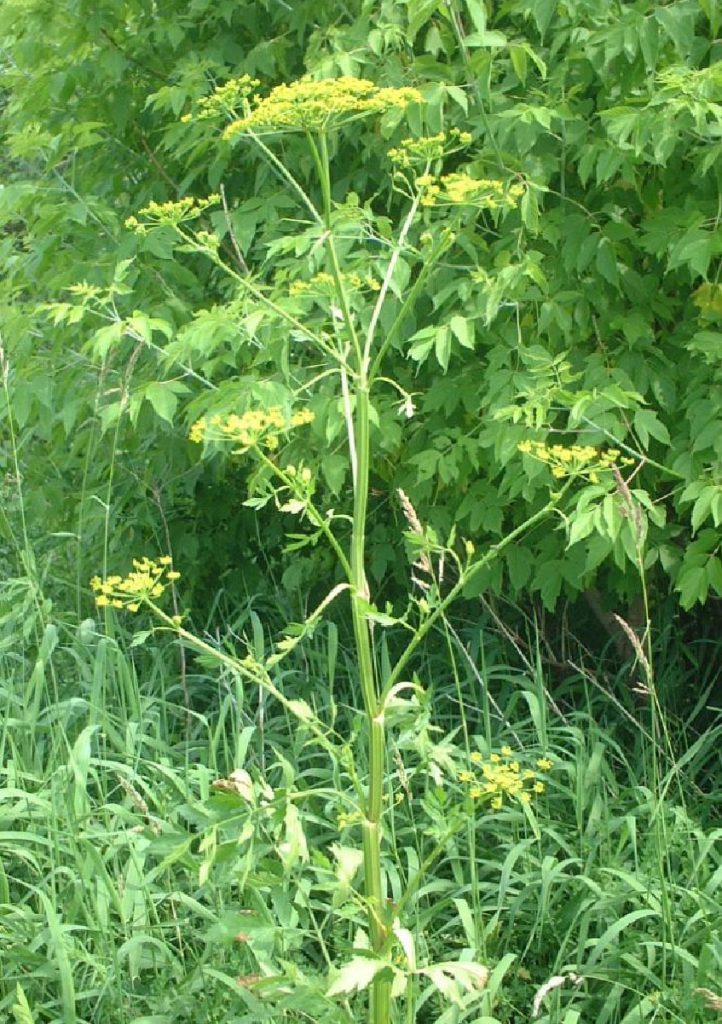
Wild Parsnip
An aggressive Eurasian member of the carrot family that grows in sunny areas with sap that can cause phytophotodermatitis.
Photo left: Common Mullein
All Articles
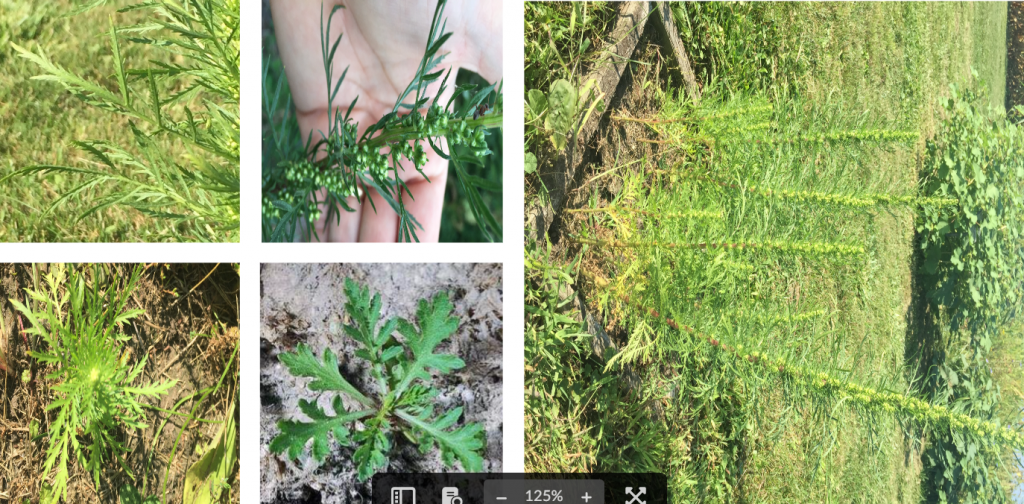
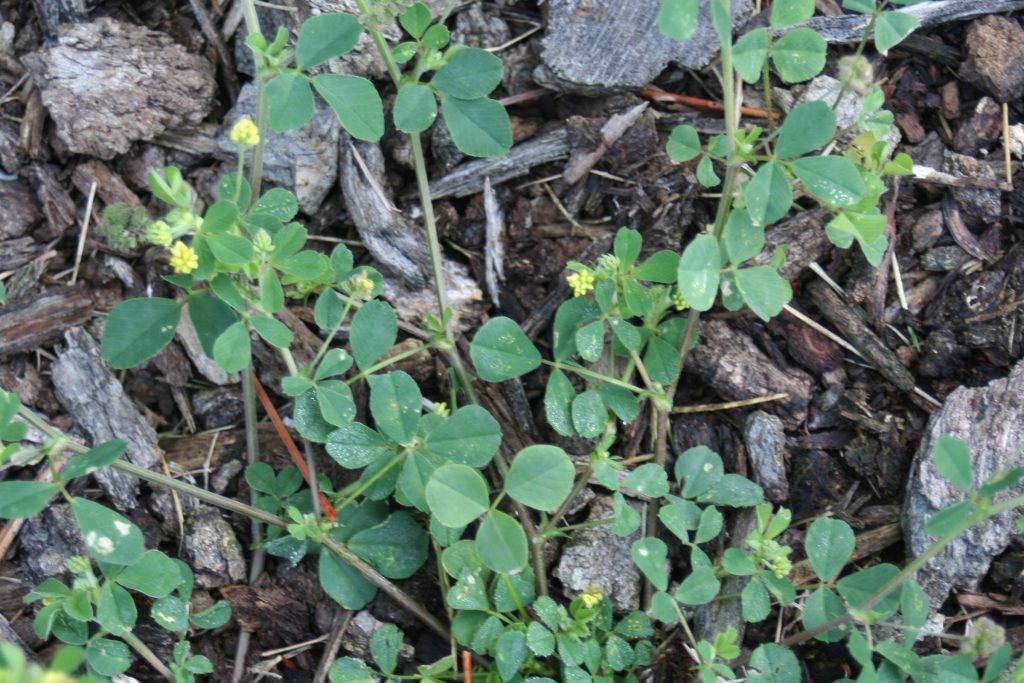
Click on any photo or name below to learn more!
For more weeds and invasive plant information, see the resources at the Renz Weed Science Lab.