Landscape Style Options
The geometric forms of buildings and natural landscaped characteristics both suggest design patterns. As a result, a home landscape that blends geometric and naturalistic patterns is often successful. Today’s landscape styles are divided into four categories in which varying proportions of geometric and naturalistic patterns are combined.
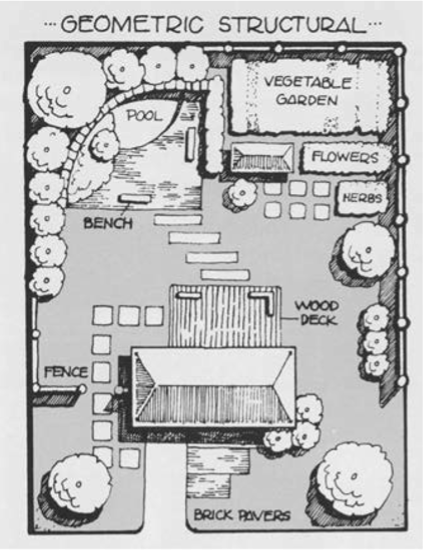
Geometric–Structural
Geometric structure is primary and plants play a minor role. Straight lines of walks, driveways, and planting beds are typically used.
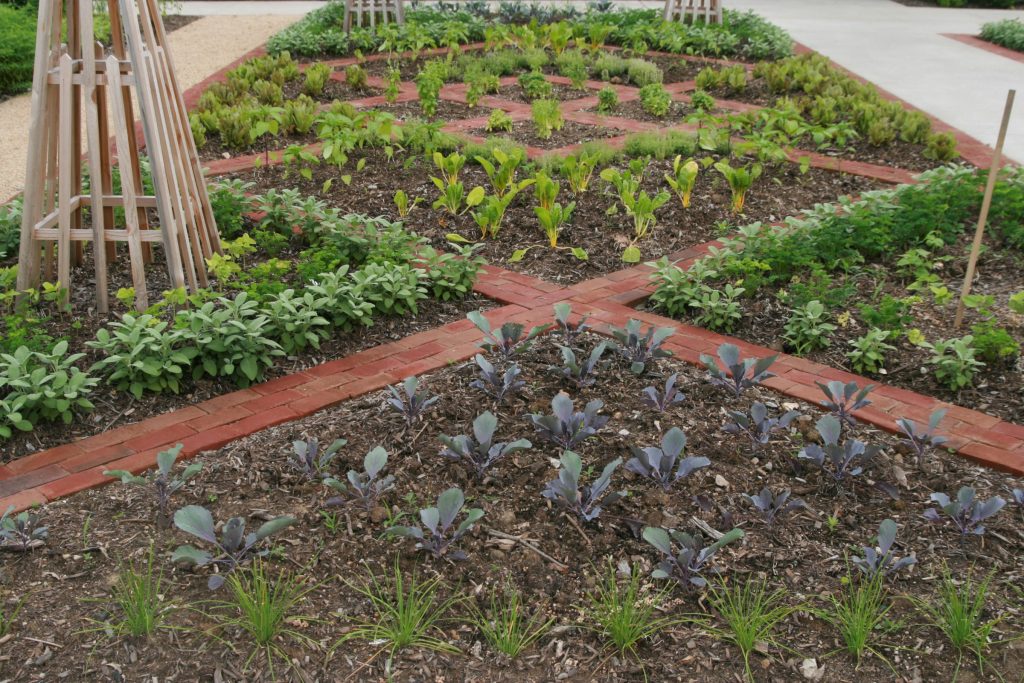
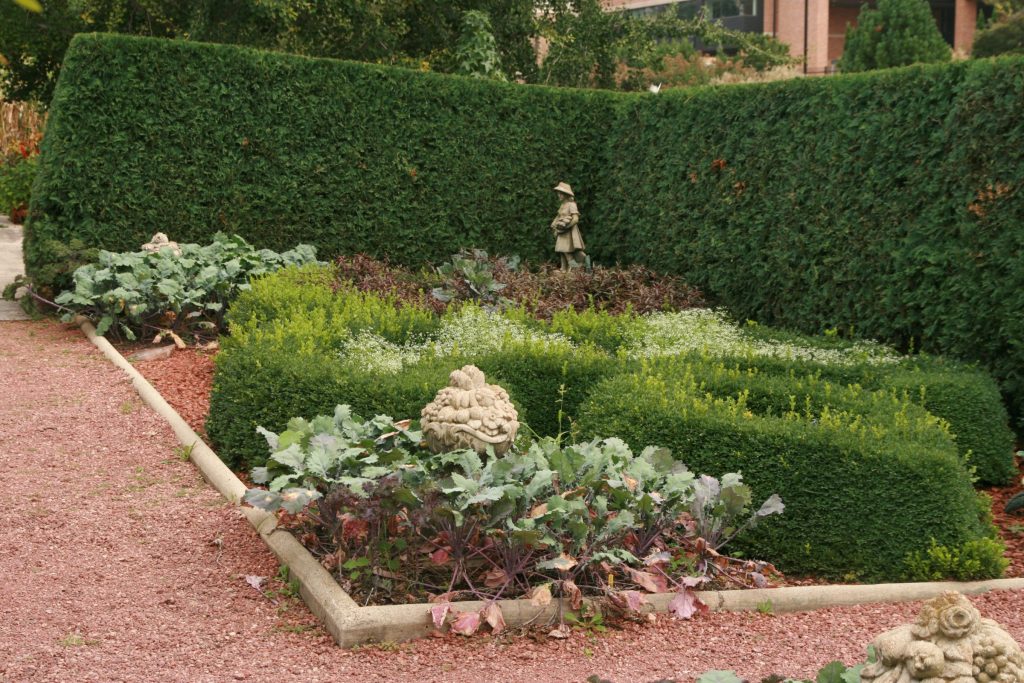
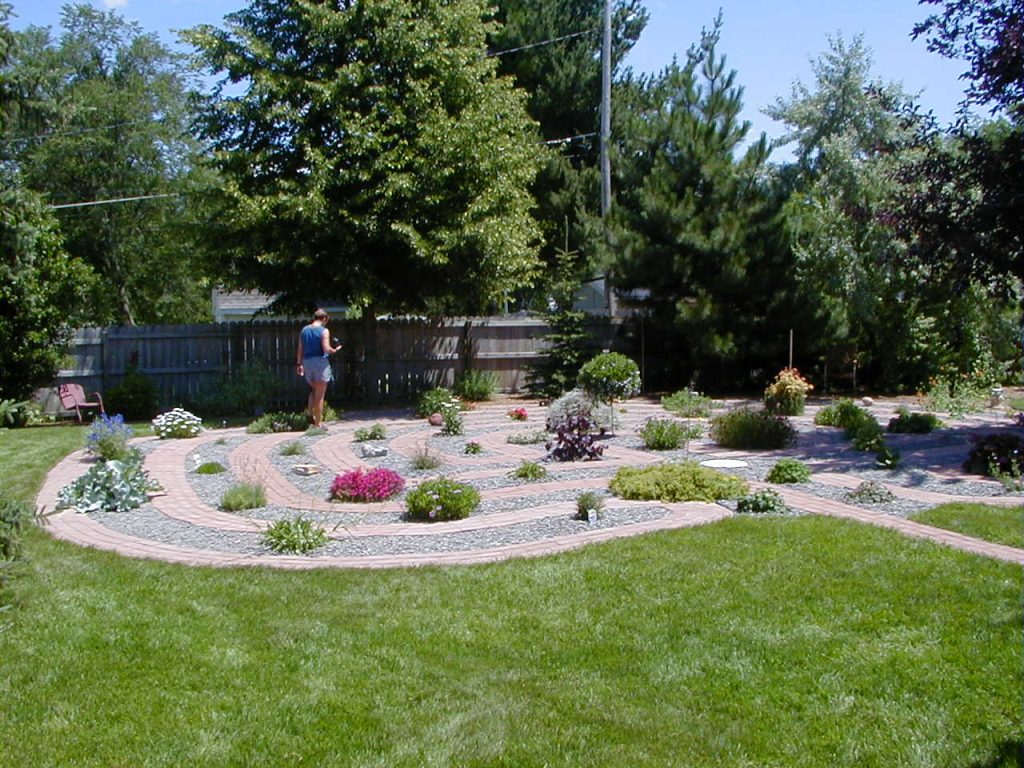
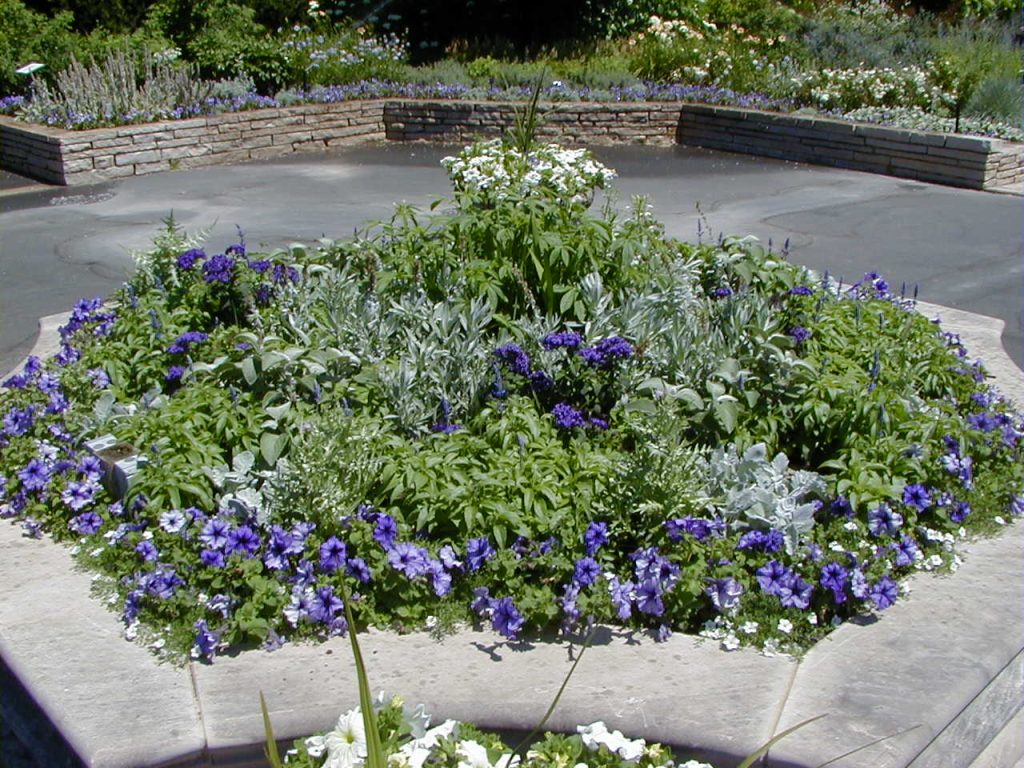




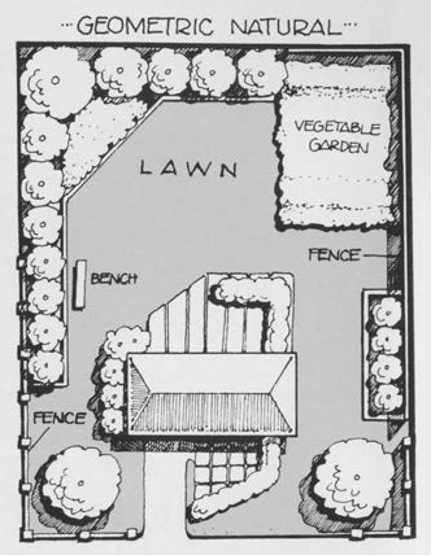
Geometric–Natural
Structure dominates, but plants and other natural elements play an important—perhaps nearly equal—role. Straight lines and more formal curves often define landscape features.
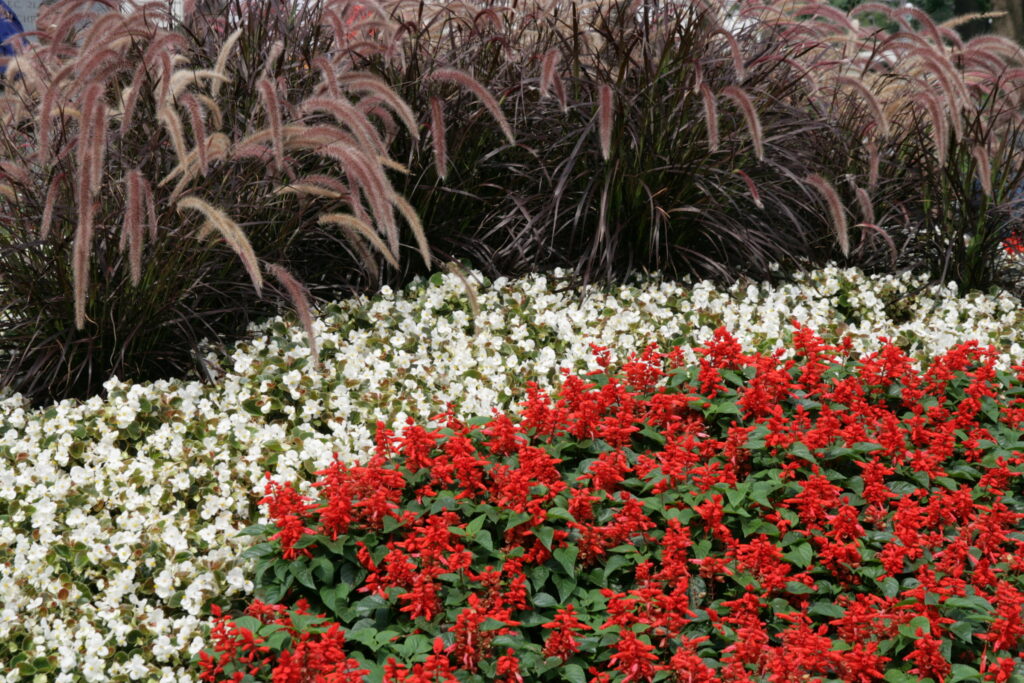
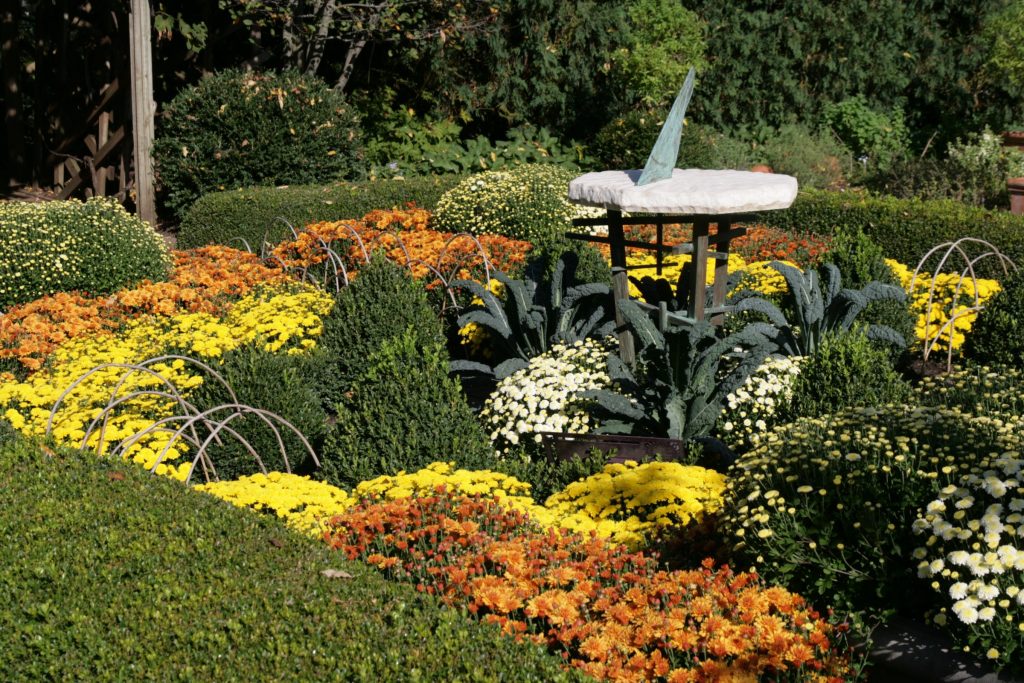
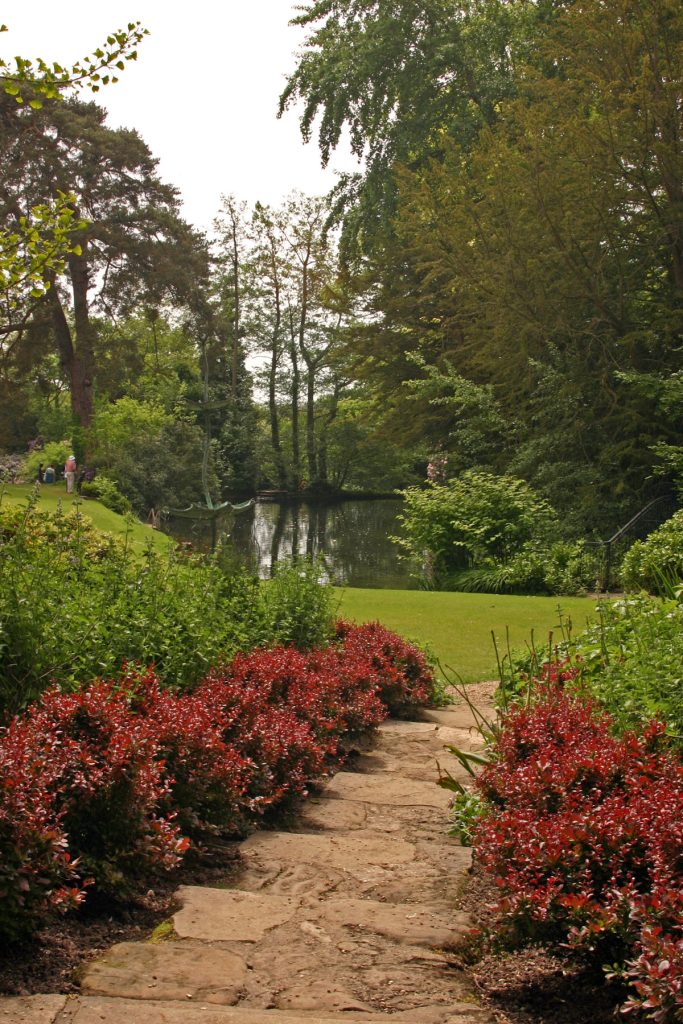
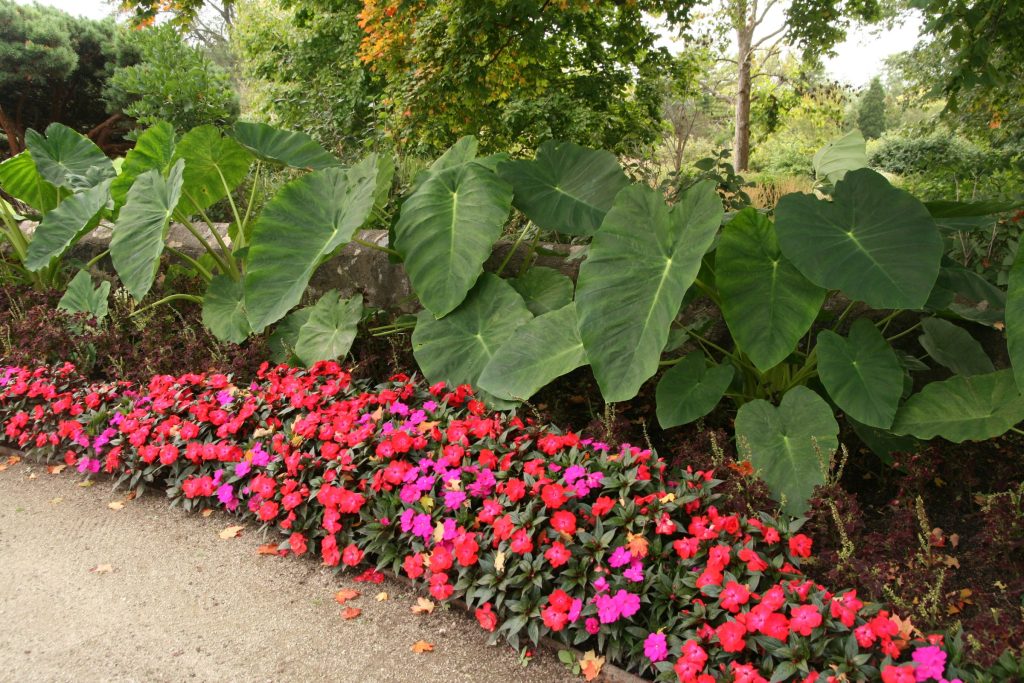




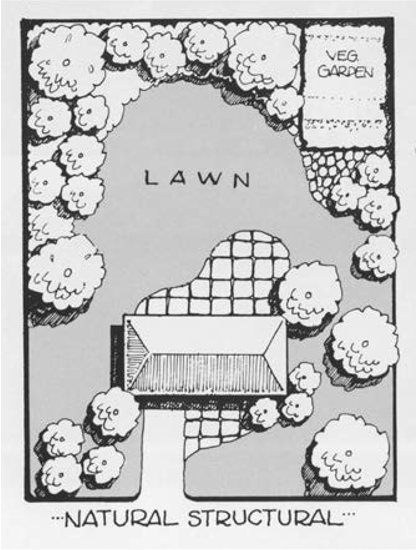
Natural-Structural
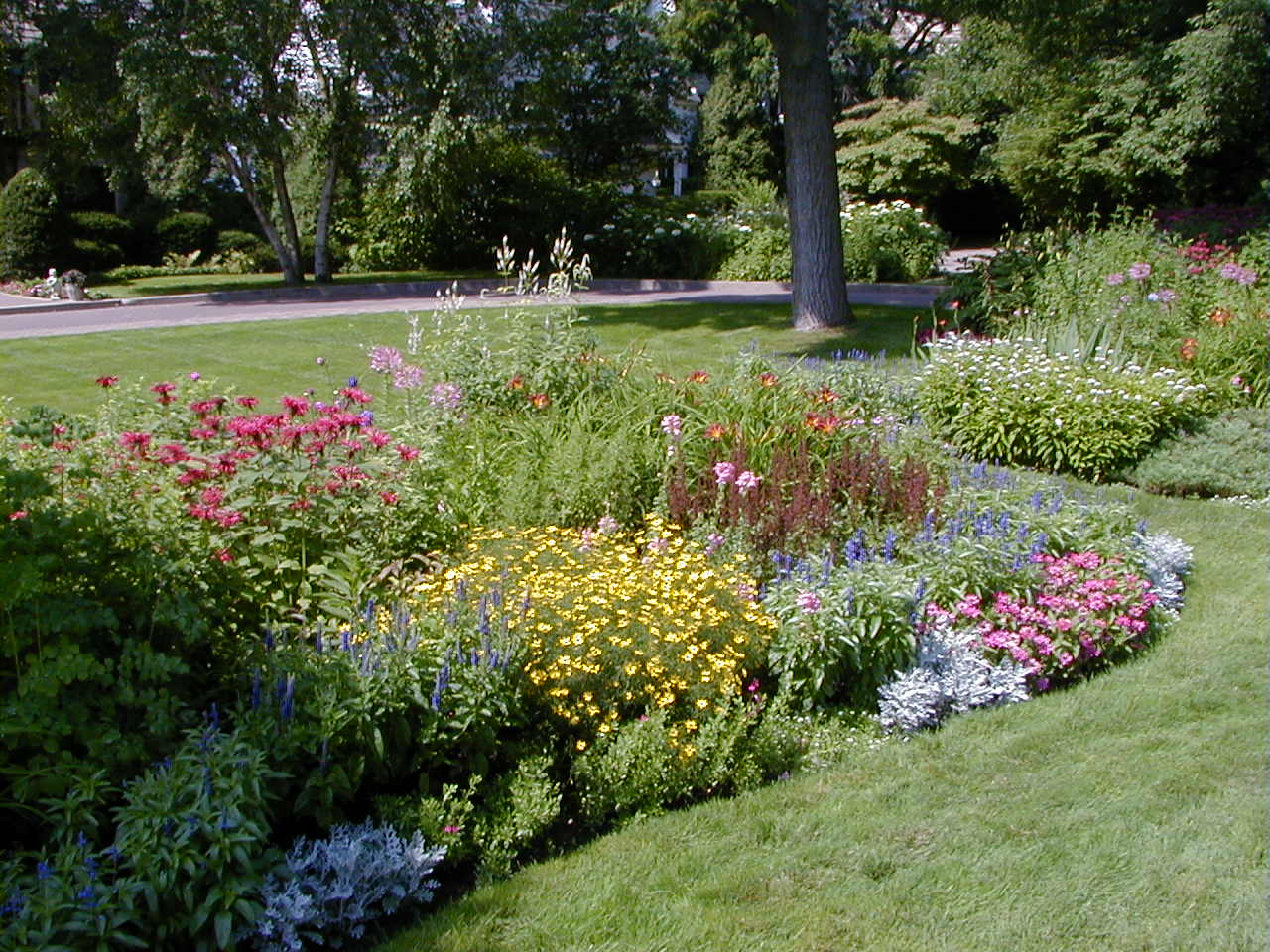
Plants, rocks, water, and earth forms dominate, but there is a clear sense of geometric arrangement. Naturally flowing, curvilinear lines are used to “soften” the transition from one area to another in the landscape.
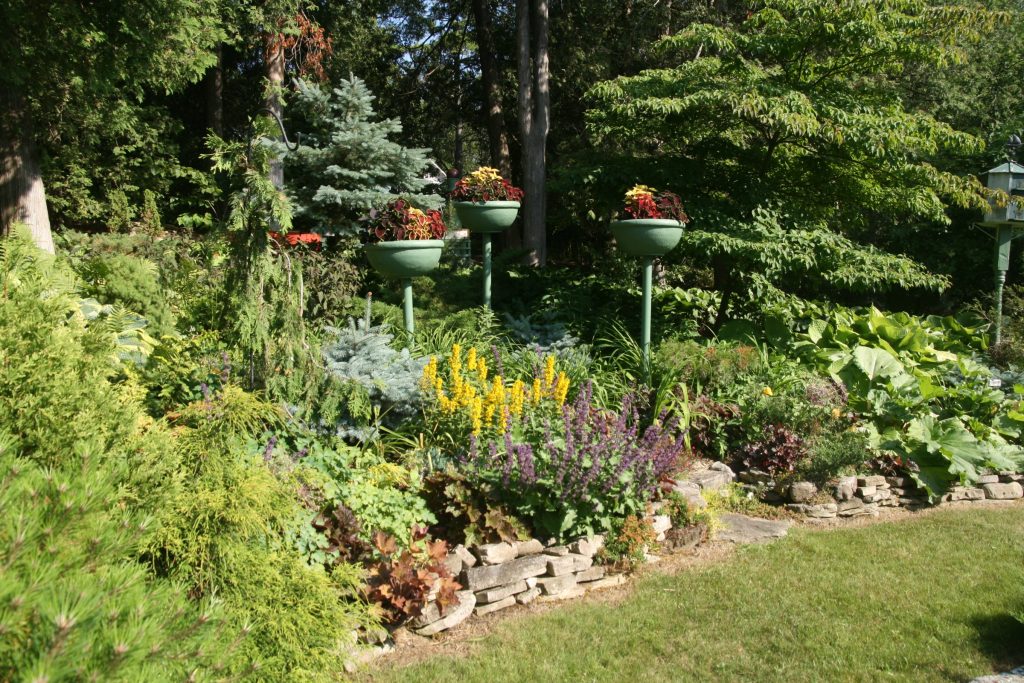
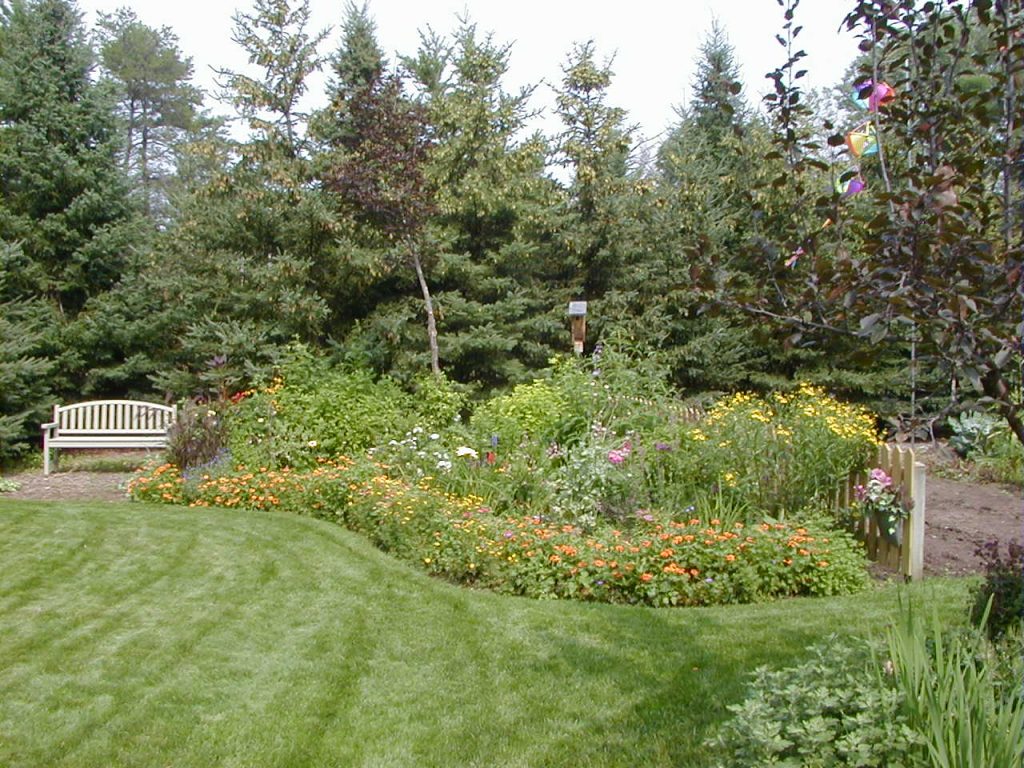
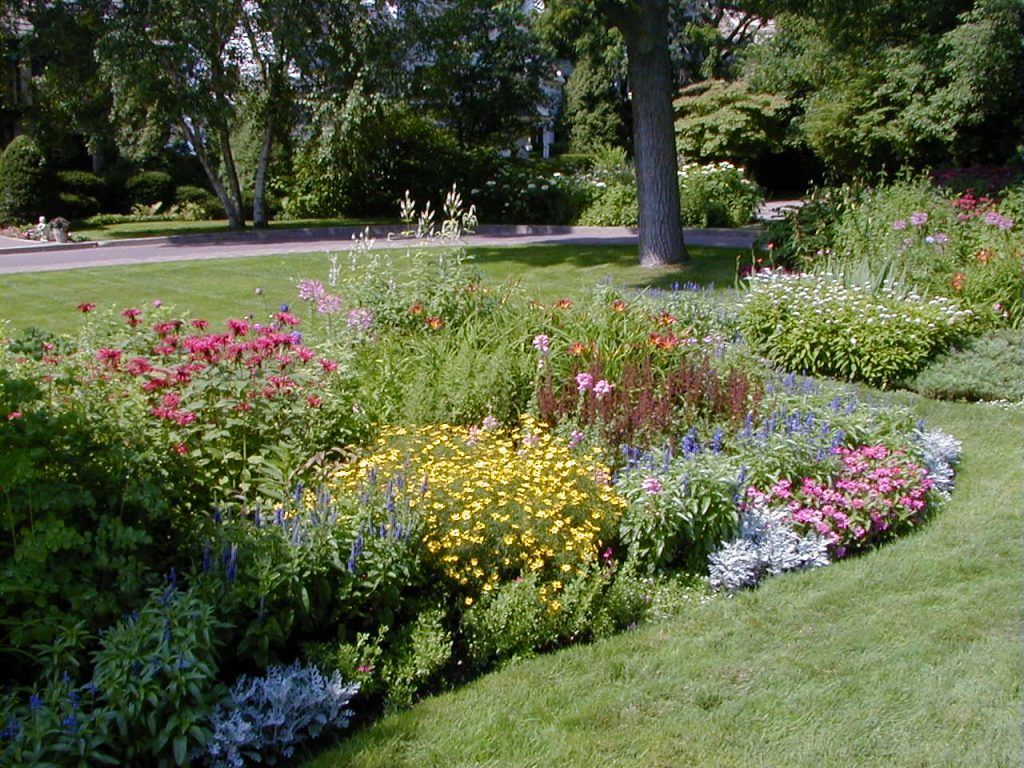
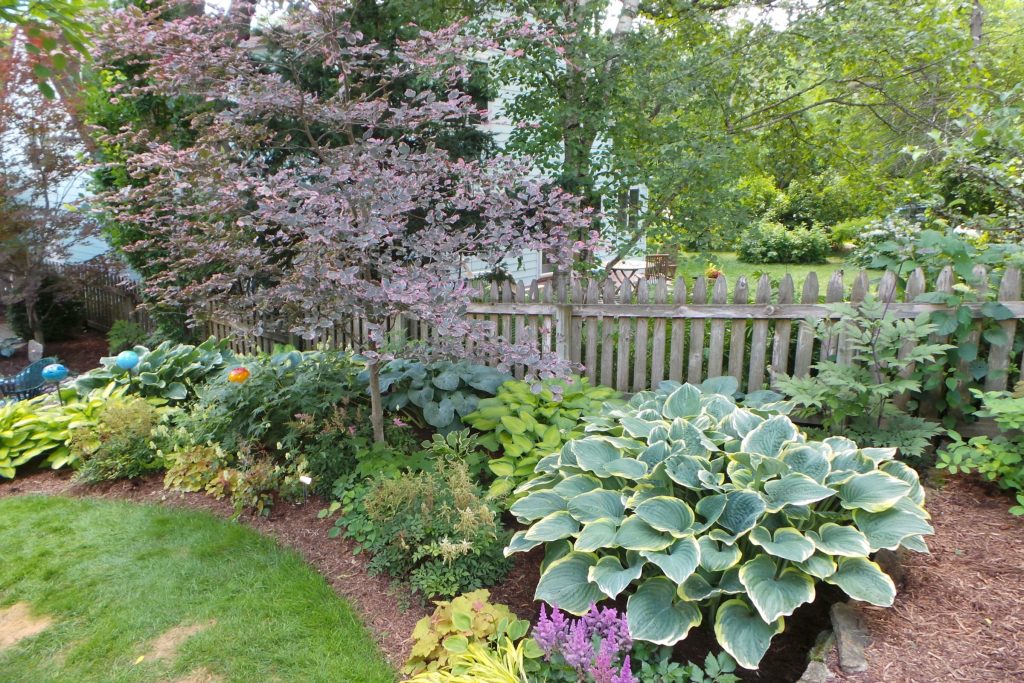




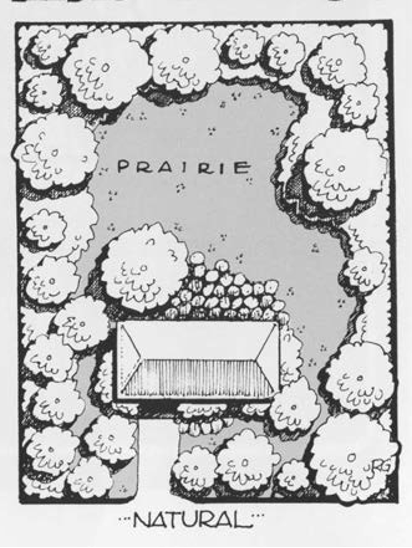
Natural
Natural elements and materials dominate, and there is no obvious human-determined form or structure. Elements in the landscape flow naturally into each other with few or no clearly defined lines.
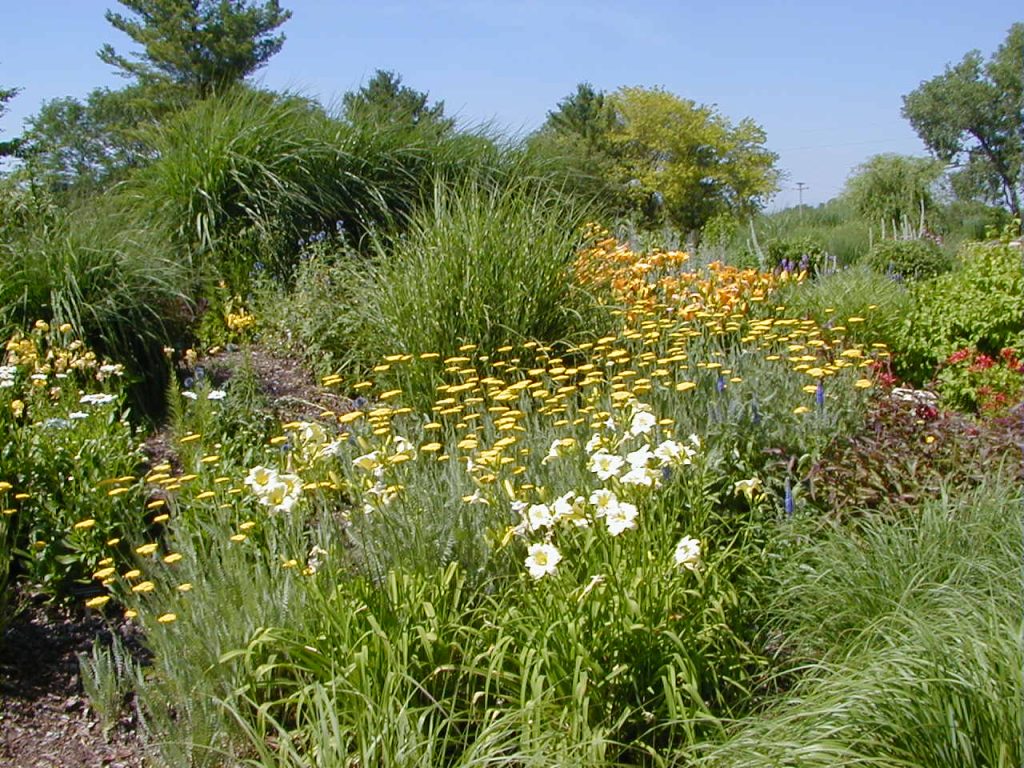
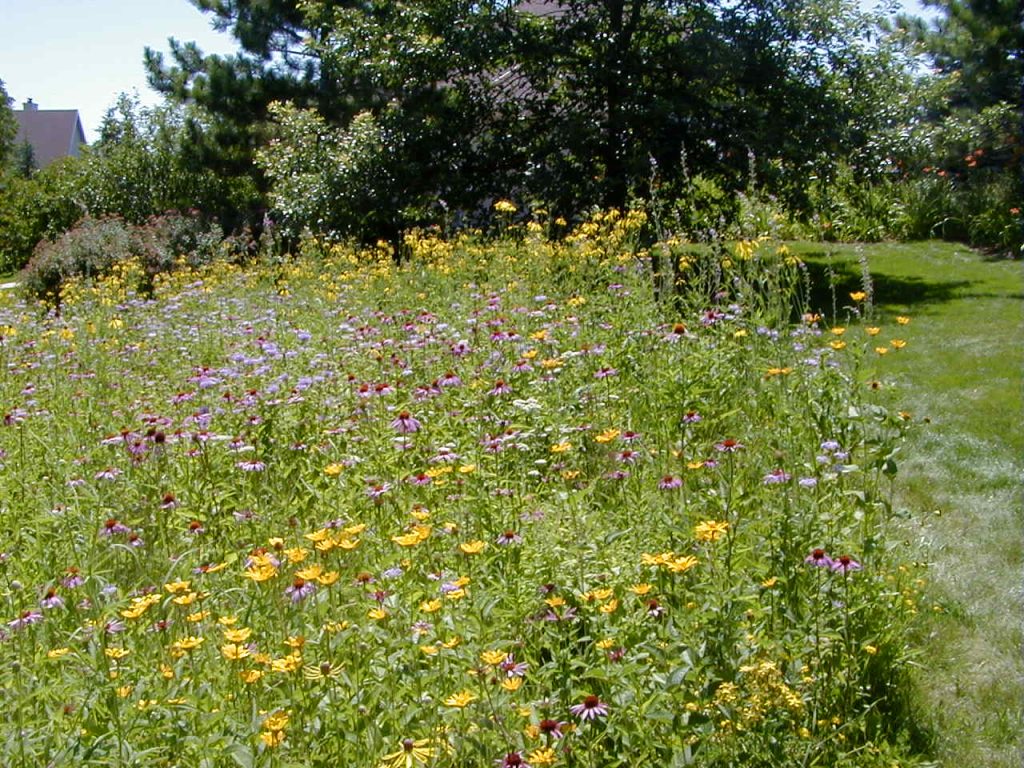
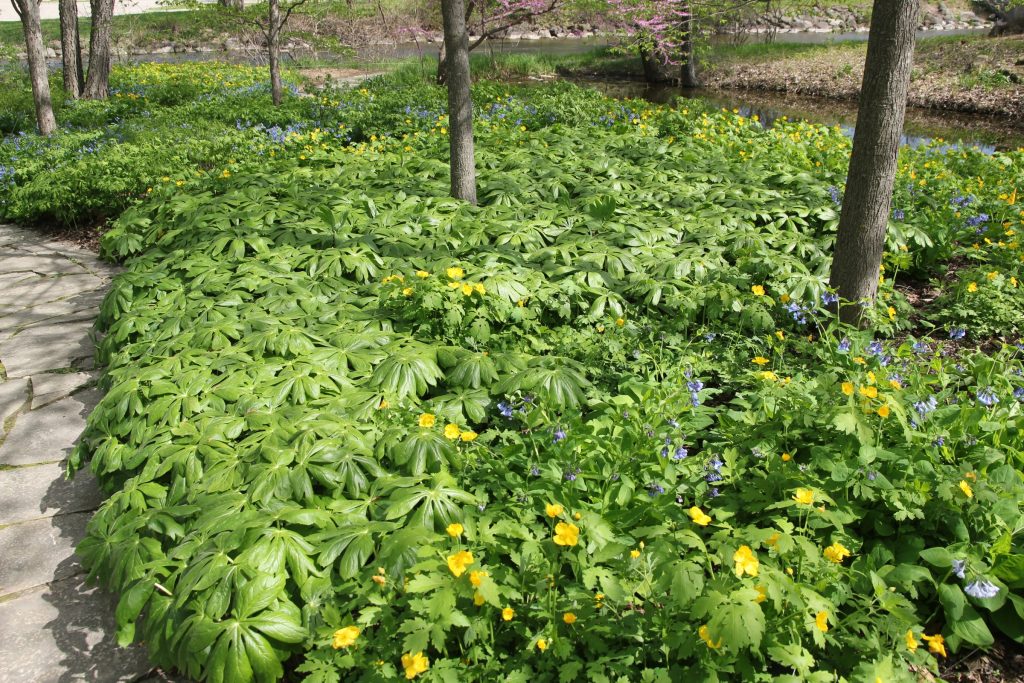
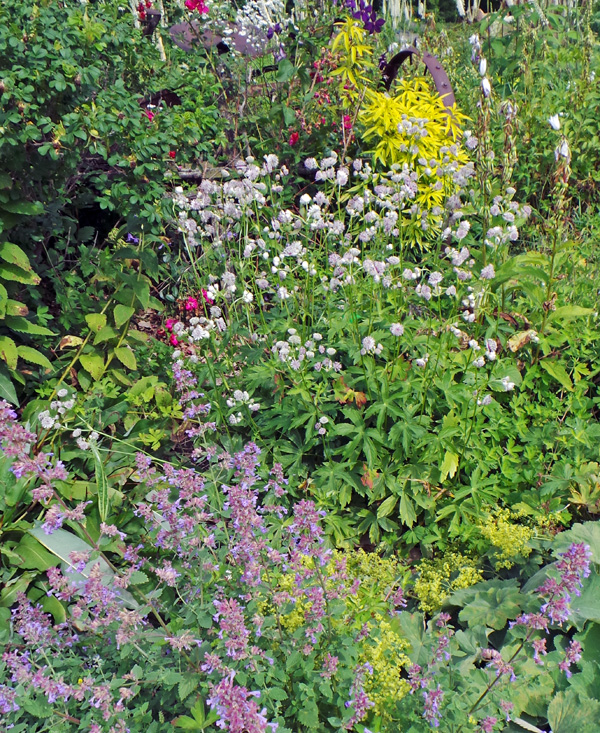




As you plan and design, think about which design style you want to achieve.
← Previous: Overview
Next: Planning →
Authors: Dan Wilson, Professors Emeritus, University of Wisconsin-Extension, Thomas Wilson, Professors Emeritus, University of Wisconsin-Extension, and Wayne Tlusty, Professor Emeritus, University of Wisconsin-Madison. Illustrations by Renee Graef.
Reviewed by: Christine Wen, UW-Extension Walworth County Horticulture Educator
Last revised: 5/10/2010
Item number: G1923
References and Additional Resources
Plant Selection
- A Guide to Selecting Landscape Plants for Wisconsin (A2865)
- Choosing the Right Landscape Plants: Factors to Consider (A3864)
- Container Gardening (A3382)
- Landscape Plants That Attract Birds (G1609)
- Lawn Establishment and Renovation (A3434)
- Lilacs for Cold Climates (A3825)
- Prairie Primer (G2736)
- Selecting Woody Landscape Plants for Fall Color: An Illustrated Guide (A3837)
Plant Care
- Caring for Deciduous Shrubs (A1771)
- Caring for Your Established Shade Trees (A1817)
- Do-It-Yourself Alternative Lawn Care (A3964)
- Growing Grass in Shade (A3700)
- Lawn Weed Prevention and Control (A1990)
- Mulches for Home Gardens and Plantings (A3383)
- Organic and Reduced-Risk Lawn Care (A3958)
- Organic Soil Conditioners (A2305)
- Sampling Garden Soils and Turf Areas for Testing (A2166)
- Selecting, Planting, and Caring for Your Shade Trees (A3067)
- Tree and Shrub Fertilization (A2308)
- Watering Your Lawn (A3950)
Yard Care and the Environment series
- Lawn and Garden Fertilizers (GWQ002)
- Lawn and Garden Pesticides (GWQ011)
- Lawn Watering (GWQ012)
- Lawn Weed Control (GWQ013)
- Managing Leaves and Yard Trimmings (GWQ022)
- Rethinking Yard Care (GWQ009)
- Shoreline Plants and Landscaping (GWQ014)
Other Publications
- Landscaping for Wildlife, available from the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources.
- Livable Landscape Design (141IB-211), available from Cornell University.